Product Description
As a professional manufacturer for propeller shaft, we have +800 items for all kinds of car, main suitable
for AMERICA & EUROPE market.
Our advantage:
1. Full range of products
2. MOQ qty: 5pcs/items
3. Delivery on time
4: Warranty: 1 YEAR
5. Develope new items: FREE
|
Brand Name |
KOWA DRIVE SHAFT |
|
Item name |
OEM |
|
Car maker |
For all japanese/korean/european/american car |
|
Moq |
5pcs |
|
Guarantee |
12 months |
|
sample |
Available if have stock |
|
Price |
Send inquiry to get lastest price |
|
BOX/QTY |
1PCS/Bag 4PCS /CTNS |
For some items, we have stock, small order (+3000USD) is welcome.
The following items are some of drive shafts, If you need more information, pls contact us for ASAP.
| For Japanese Car | |||
| for TOYOTA | for TOYOTA | ||
| 43420-57170 | 43420-57180 | 43410-0W081 | 43420-0W080 |
| 43410-57120 | 43420-57190 | 43410-0W091 | 43420-0W090 |
| 43410-57130 | 43420-57120 | 43410-0W100 | 43420-0W110 |
| 43410-57150 | 43420-02B10 | 43410-0W110 | 43420-0W160 |
| 43410-06221 | 43420-02B11 | 43410-0W140 | 43420-32161 |
| 43410-06231 | 43420-02B60 | 43410-0W150 | 43420-33250 |
| 43410-06460 | 43420-02B61 | 43410-0W180 | 43420-33280 |
| 43410-06570 | 43420-02B62 | 43410-12410 | 43420-48090 |
| 43410-06580 | 43420-06221 | 43410-33280 | 43420-48091 |
| 43410-066-90 | 43420-06231 | 43410-33290 | 43430OK571 |
| 43410-06750 | 43420-06460 | 43410-33330 | 66-5245 |
| 43410-06780 | 43420-06490 | 43410-48070 | 66-5247 |
| 43410-06A40 | 43420-06500 | 43410-48071 | 43420-57150 |
| 43410-06A50 | 43420- 0571 0 | 43410-0W061 | 43420-0W061 |
| 43410-07070 | 43420-06610 | 43410-0W071 | 43420-0W071 |
| for Acura | for LEXUS | ||
| 44305STKA00 | 66-4198 | 43410-06200 | 43410-06480 |
| 44305STKA01 | 66-4261 | 43410-06450 | 43410-06560 |
| 44305SZPA00 | 66-4262 | 66-5265 | |
| 44306STKA00 | 66-4270 | for MITSUBISHI | |
| 44306STKA01 | 66-4271 | 3815A309 | 3815A310 |
| 44306SZPA00 | |||
| for Honda | for MAZDA | ||
| 44571S1571 | 44306S3VA61 | 5L8Z3A428AB | GG052550XD |
| 44011S1571 | 44306S3VA62 | 5L8Z3A428DA | GG052560XE |
| 44305S2HN50 | 44306S9VA51 | 66-2090 | GG362550XA |
| 44305SCVA50 | 44306S9VA71 | 6L8Z3A428A | YL8Z3A427AA |
| 44305SCVA51 | 44306SCVA50 | 9L8Z3A427B | YL8Z3A427BA |
| 44305SCVA90 | 44306SCVA51 | GG032550XD | YL8Z3A428AA |
| 44305SCVA91 | 44306SCVA90 | GG042550XD | YL8Z3A428BA |
| 44305STXA02 | 44306SCVA91 | GG042560XG | ZC32550XA |
| 44305SZAA01 | 44306STXA02 | for Nissan | |
| 44306S2H951 | 44306SZAA01 | 39101-1HS0A | 39100-1HS0A |
| 44306SZAA11 | 44306SZAA01RM | 39101-1HS0B | 39100-1HS0B |
| 44306SZAA12 | 66-4213 | ||
| 66-4214 | |||
| for Europe Car | |||
| for VOLKSWAGEN | for VOLKSWAGEN | ||
| 4885712AD | 7B0407271B | 7E0407271G | 7LA407272C |
| 4885713AF | 7B0407272 | 7E0407271P | 7LA4 0571 2CX |
| 4881214AE | 7B0407272E | 7LA407271E | |
| 7B0407271A | |||
| for America Car | |||
| for CHRYSLER | for MERCURY | ||
| 4593447AA | 557180AD | 4F1Z3B437AA | GG322560X |
| 4641855AA | 52114390AB | 5L8Z3A428DB | GG362560XA |
| 4641855AC | 5273546AC | 66-2249 | YL8Z3A427CA |
| 4641856AA | 66-3108 | 9L8Z3A427C | YL8Z3A427DA |
| 4641856AC | 66-3109 | 9L8Z3A427D | YL8Z3A427EA |
| 4882517 | 66-3130 | GG062550XD | YL8Z3A427FA |
| 4882518 | 66-3131 | GG062560XE | YL8Z3A428CA |
| 4882519 | 66-3234 | GG312560X | ZZDA2560X |
| 4882520 | 66-3518 | ZZDA2560XC | ZZDA2560XA |
| 557130AB | 66-3520 | for RAM | |
| 66-3552 | 66-3522 | 4885713AD | 55719AB |
| 66-3553 | 66-3551 | 4881214AD | 66-3404 |
| 66-3554 | 66-3639 | 55719AA | 66-3740 |
| 68193908AB | 66-3641 | 68571398AA | |
| for FORD | for DODGE | ||
| 1F0571400 | E6DZ3V428AARM | 4593449AA | 7B0407272A |
| 1F0571410 | E8DZ3V427AARM | 4641855AE | 7B0407272B |
| 1F2Z3B436AA | E8DZ3V428AARM | 4641855EE | 7B0407272C |
| 2F1Z3A428CA | E90Y3V427AARM | 4641856AD | R4881214AE |
| 2M5Z3B437CA | E90Y3V428AARM | 4641856AF | RL189279AA |
| 4F1Z3B437BA | F0DZ3V427AARM | 4885710AC | 557180AG |
| 5M6Z3A428AA | F0DZ3V428AARM | 4885710AE | 5170822AA |
| 5S4Z3B437AA | F21Z3B437A | 4885710AF | 52114390AA |
| 66-2005 | F21Z3B437B | 4885710AG | 5273546AD |
| 66-2008 | F2DZ3B436A | 4885711AC | 5273546AE |
| 66-2571 | F2DZ3B436B | 4885711AD | 5273546AF |
| 66-2084 | F2DZ3B437A | 4885712AC | 5273558AB |
| 66-2086 | F2DZ3B437B | 4885712AE | 5273558AD |
| 66-2095 | F4DZ3B437A | 4885712AG | 5273558AE |
| 66-2101 | F57Z3B436BA | 4885712AH | 5273558AF |
| 66-2143 | F57Z3B437BA | 4885713AC | 4881214AC |
| 6S4Z3B437BA | F5DZ3A427BA | 4885713AG | 4881214AF |
| 8S4Z3B437A | F5DZ3A428AS | 4885713AI | 4881214AG |
| 9L8Z3A427A | F5DZ3B426D | 4885713AJ | 557130AA |
| E6DZ3V427AARM | F5DZ3B436D | 5273558AG | 557180AE |
| YF1Z3A428RS | F5DZ3B437B | 66-3382 | 557180AF |
| YL8Z3A428DA | F5TZ3B436A | 66-3511 | 66-3514 |
| YS4Z3B437BB | GG032560XG | 66-3759 | 66-3564 |
| YS4Z3B437CB | GG362550X | ||
| YF1Z3A427L | |||
| for CHEVROLET | for JEEP | ||
| 257191 | 26062613 | 4578885AA | 5215710AA |
| 22791460 | 4578885AB | 5215711AB | |
| 26011961 | 4578885AC | 5215711AB | |
| 26571730 | 2657189 | 4720380 | 5273438AC |
| 2657165 | 66-1401 | 4720381 | 5273438AD |
| 26058932 | 66-1438 | 5012456AB | 5273438AE |
| 26065719 | 88982496 | 5012457AB | 5273438AG |
| for HUMMER | 5066571AA | 66-3220 | |
| 1571204 | 595716 | 557120AB | 66-3221 |
| 15886012 | 66-1417 | 557120AC | 66-3298 |
| for CADILLAC | 557120AD | 66-3352 | |
| 88957151 | 66-1416 | 557120AE | 66-3417 |
| 66-1009 | 66-1430 | 5189278AA | 66-3418 |
| 66-1415 | 88957150 | 5189279AA | 66-3419 |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | ISO |
| Type: | Drive Shaft |
| Application Brand: | Nissan |
| Samples: |
US$ 300/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
How do drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance?
Drive shafts employ various mechanisms to ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance. Efficient power transfer refers to the ability of the drive shaft to transmit rotational power from the source (such as an engine) to the driven components (such as wheels or machinery) with minimal energy loss. Balancing, on the other hand, involves minimizing vibrations and eliminating any uneven distribution of mass that can cause disturbances during operation. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts achieve both efficient power transfer and balance:
1. Material Selection:
The material selection for drive shafts is crucial for maintaining balance and ensuring efficient power transfer. Drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their strength, stiffness, and durability. These materials have excellent dimensional stability and can withstand the torque loads encountered during operation. By using high-quality materials, drive shafts can minimize deformation, flexing, and imbalances that could compromise power transmission and generate vibrations.
2. Design Considerations:
The design of the drive shaft plays a significant role in both power transfer efficiency and balance. Drive shafts are engineered to have appropriate dimensions, including diameter and wall thickness, to handle the anticipated torque loads without excessive deflection or vibration. The design also considers factors such as the length of the drive shaft, the number and type of joints (such as universal joints or constant velocity joints), and the use of balancing weights. By carefully designing the drive shaft, manufacturers can achieve optimal power transfer efficiency while minimizing the potential for imbalance-induced vibrations.
3. Balancing Techniques:
Balance is crucial for drive shafts as any imbalance can cause vibrations, noise, and accelerated wear. To maintain balance, drive shafts undergo various balancing techniques during the manufacturing process. Static and dynamic balancing methods are employed to ensure that the mass distribution along the drive shaft is uniform. Static balancing involves adding counterweights at specific locations to offset any weight imbalances. Dynamic balancing is performed by spinning the drive shaft at high speeds and measuring any vibrations. If imbalances are detected, additional adjustments are made to achieve a balanced state. These balancing techniques help minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation of the drive shaft.
4. Universal Joints and Constant Velocity Joints:
Drive shafts often incorporate universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints to accommodate misalignment and maintain balance during operation. U-joints are flexible joints that allow for angular movement between shafts. They are typically used in applications where the drive shaft operates at varying angles. CV joints, on the other hand, are designed to maintain a constant velocity of rotation and are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles. By incorporating these joints, drive shafts can compensate for misalignment, reduce stress on the shaft, and minimize vibrations that can negatively impact power transfer efficiency and balance.
5. Maintenance and Inspection:
Regular maintenance and inspection of drive shafts are essential for ensuring efficient power transfer and balance. Periodic checks for wear, damage, or misalignment can help identify any issues that may affect the drive shaft’s performance. Lubrication of the joints and proper tightening of fasteners are also critical for maintaining optimal operation. By adhering to recommended maintenance procedures, any imbalances or inefficiencies can be addressed promptly, ensuring continued efficient power transfer and balance.
In summary, drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance through careful material selection, thoughtful design considerations, balancing techniques, and the incorporation of flexible joints. By optimizing these factors, drive shafts can transmit rotational power smoothly and reliably, minimizing energy losses and vibrations that can impact performance and longevity.

How do drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks?
Drive shafts play a significant role in enhancing the performance of automobiles and trucks. They contribute to various aspects of vehicle performance, including power delivery, traction, handling, and overall efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks:
1. Power Delivery:
Drive shafts are responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move forward. By efficiently transmitting power without significant losses, drive shafts ensure that the engine’s power is effectively utilized, resulting in improved acceleration and overall performance. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal power loss contribute to the vehicle’s ability to deliver power to the wheels efficiently.
2. Torque Transfer:
Drive shafts facilitate the transfer of torque from the engine to the wheels. Torque is the rotational force that drives the vehicle forward. High-quality drive shafts with proper torque conversion capabilities ensure that the torque generated by the engine is effectively transmitted to the wheels. This enhances the vehicle’s ability to accelerate quickly, tow heavy loads, and climb steep gradients, thereby improving overall performance.
3. Traction and Stability:
Drive shafts contribute to the traction and stability of automobiles and trucks. They transmit power to the wheels, allowing them to exert force on the road surface. This enables the vehicle to maintain traction, especially during acceleration or when driving on slippery or uneven terrain. The efficient power delivery through the drive shafts enhances the vehicle’s stability by ensuring balanced power distribution to all wheels, improving control and handling.
4. Handling and Maneuverability:
Drive shafts have an impact on the handling and maneuverability of vehicles. They help establish a direct connection between the engine and the wheels, allowing for precise control and responsive handling. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal play or backlash contribute to a more direct and immediate response to driver inputs, enhancing the vehicle’s agility and maneuverability.
5. Weight Reduction:
Drive shafts can contribute to weight reduction in automobiles and trucks. Lightweight drive shafts made from materials such as aluminum or carbon fiber-reinforced composites reduce the overall weight of the vehicle. The reduced weight improves the power-to-weight ratio, resulting in better acceleration, handling, and fuel efficiency. Additionally, lightweight drive shafts reduce the rotational mass, allowing the engine to rev up more quickly, further enhancing performance.
6. Mechanical Efficiency:
Efficient drive shafts minimize energy losses during power transmission. By incorporating features such as high-quality bearings, low-friction seals, and optimized lubrication, drive shafts reduce friction and minimize power losses due to internal resistance. This enhances the mechanical efficiency of the drivetrain system, allowing more power to reach the wheels and improving overall vehicle performance.
7. Performance Upgrades:
Drive shaft upgrades can be a popular performance enhancement for enthusiasts. Upgraded drive shafts, such as those made from stronger materials or with enhanced torque capacity, can handle higher power outputs from modified engines. These upgrades allow for increased performance, such as improved acceleration, higher top speeds, and better overall driving dynamics.
8. Compatibility with Performance Modifications:
Performance modifications, such as engine upgrades, increased power output, or changes to the drivetrain system, often require compatible drive shafts. Drive shafts designed to handle higher torque loads or adapt to modified drivetrain configurations ensure optimal performance and reliability. They enable the vehicle to effectively harness the increased power and torque, resulting in improved performance and responsiveness.
9. Durability and Reliability:
Robust and well-maintained drive shafts contribute to the durability and reliability of automobiles and trucks. They are designed to withstand the stresses and loads associated with power transmission. High-quality materials, appropriate balancing, and regular maintenance help ensure that drive shafts operate smoothly, minimizing the risk of failures or performance issues. Reliable drive shafts enhance the overall performance by providing consistent power delivery and minimizing downtime.
10. Compatibility with Advanced Technologies:
Drive shafts are evolving in tandem with advancements in vehicle technologies. They are increasingly being integrated with advanced systems such as hybrid powertrains, electric motors, and regenerative braking. Drive shafts designed to work seamlessly with these technologies maximize their efficiency and performance benefits, contributing to improved overall vehicle performance.
In summary, drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks by optimizing power delivery, facilitating torque transfer, improving traction and stability, enhancing handling and maneuverability, reducing weight, increasing mechanical efficiency,and enabling compatibility with performance upgrades and advanced technologies. They play a crucial role in ensuring efficient power transmission, responsive acceleration, precise handling, and overall improved performance of vehicles.
Are there variations in drive shaft designs for different types of machinery?
Yes, there are variations in drive shaft designs to cater to the specific requirements of different types of machinery. The design of a drive shaft is influenced by factors such as the application, power transmission needs, space limitations, operating conditions, and the type of driven components. Here’s an explanation of how drive shaft designs can vary for different types of machinery:
1. Automotive Applications:
In the automotive industry, drive shaft designs can vary depending on the vehicle’s configuration. Rear-wheel-drive vehicles typically use a single-piece or two-piece drive shaft, which connects the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential. Front-wheel-drive vehicles often use a different design, employing a drive shaft that combines with the constant velocity (CV) joints to transmit power to the front wheels. All-wheel-drive vehicles may have multiple drive shafts to distribute power to all wheels. The length, diameter, material, and joint types can differ based on the vehicle’s layout and torque requirements.
2. Industrial Machinery:
Drive shaft designs for industrial machinery depend on the specific application and power transmission requirements. In manufacturing machinery, such as conveyors, presses, and rotating equipment, drive shafts are designed to transfer power efficiently within the machine. They may incorporate flexible joints or use a splined or keyed connection to accommodate misalignment or allow for easy disassembly. The dimensions, materials, and reinforcement of the drive shaft are selected based on the torque, speed, and operating conditions of the machinery.
3. Agriculture and Farming:
Agricultural machinery, such as tractors, combines, and harvesters, often requires drive shafts that can handle high torque loads and varying operating angles. These drive shafts are designed to transmit power from the engine to attachments and implements, such as mowers, balers, tillers, and harvesters. They may incorporate telescopic sections to accommodate adjustable lengths, flexible joints to compensate for misalignment during operation, and protective shielding to prevent entanglement with crops or debris.
4. Construction and Heavy Equipment:
Construction and heavy equipment, including excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and cranes, require robust drive shaft designs capable of transmitting power in demanding conditions. These drive shafts often have larger diameters and thicker walls to handle high torque loads. They may incorporate universal joints or CV joints to accommodate operating angles and absorb shocks and vibrations. Drive shafts in this category may also have additional reinforcements to withstand the harsh environments and heavy-duty applications associated with construction and excavation.
5. Marine and Maritime Applications:
Drive shaft designs for marine applications are specifically engineered to withstand the corrosive effects of seawater and the high torque loads encountered in marine propulsion systems. Marine drive shafts are typically made from stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials. They may incorporate flexible couplings or dampening devices to reduce vibration and mitigate the effects of misalignment. The design of marine drive shafts also considers factors such as shaft length, diameter, and support bearings to ensure reliable power transmission in marine vessels.
6. Mining and Extraction Equipment:
In the mining industry, drive shafts are used in heavy machinery and equipment such as mining trucks, excavators, and drilling rigs. These drive shafts need to withstand extremely high torque loads and harsh operating conditions. Drive shaft designs for mining applications often feature larger diameters, thicker walls, and specialized materials such as alloy steel or composite materials. They may incorporate universal joints or CV joints to handle operating angles, and they are designed to be resistant to abrasion and wear.
These examples highlight the variations in drive shaft designs for different types of machinery. The design considerations take into account factors such as power requirements, operating conditions, space constraints, alignment needs, and the specific demands of the machinery or industry. By tailoring the drive shaft design to the unique requirements of each application, optimal power transmission efficiency and reliability can be achieved.


editor by CX 2024-04-04
China wholesaler 3872810202 Output Shaft Cover for Beiben Front Axle Drive Truck Spare Parts
Product Description
Product Description
OUTPUT SHAFT COVER FOR BEIBEN FRONT AXLE DRIVE TRUCK,TRAILER,TRACTO
PART NUMBER:
86CL6395FO 86CL6089FO
70CL6081FOB 86CL6081F2 70CL6082FOB 3151
3303
014255713 A
0142508803 014255713
LRS0571 LRS00922 LRS819 LRS922 LRT0 0571 LRT668
Detailed Photos
WAREHOUSE CORNER:
We have factory to produce all kinds of clutch plate,clutch pressure,clutch disc for heavy duty truck,light truck,tractor..
We can also produce according to drawing or samples.
Packaging & Shipping
1. Packaging details: carton and wooden box packaging,woven bag,brown box, or
according to customer requirements.
2. Delivery Period: 7-30 working days after
receiving 30% deposit byTT
3. Port: HangZhou Port,China.
4. Transport: By sea, by
air,DHL,FEDEX,UPS,TNT,
FAQ
1.Q:About the payment term.
A: We can accept TT,LC,PAYPAL,WESTERNUION,and so on
2.Q:About the Quality and price
A: We supply good quality products to all our customers,give the competitive price.
3.Q:About the warranty period
A:At least half year, some parts are even longer.
4. Q:How to make order ?
A:Customer can contact us online,or send email with detail inquiry list,then we can reply soon
5.Q:About the discount
A:If the quantity large,we will give resonalbe discount.And for long time cooperation customer,we can give credit support
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Free Change for Quality Problem |
|---|---|
| Application: | Truck, Tractor, Special Truck, Trailer |
| Material: | Steel |
| Quality: | Original Quality;Good Quality |
| Package: | Export Standard Box or According to Customer Requi |
| Origina: | China |

Are there any limitations or disadvantages associated with drive shafts?
While drive shafts are widely used and offer several advantages, they also have certain limitations and disadvantages that should be considered. Here’s a detailed explanation of the limitations and disadvantages associated with drive shafts:
1. Length and Misalignment Constraints:
Drive shafts have a maximum practical length due to factors such as material strength, weight considerations, and the need to maintain rigidity and minimize vibrations. Longer drive shafts can be prone to increased bending and torsional deflection, leading to reduced efficiency and potential driveline vibrations. Additionally, drive shafts require proper alignment between the driving and driven components. Misalignment can cause increased wear, vibrations, and premature failure of the drive shaft or its associated components.
2. Limited Operating Angles:
Drive shafts, especially those using U-joints, have limitations on operating angles. U-joints are typically designed to operate within specific angular ranges, and operating beyond these limits can result in reduced efficiency, increased vibrations, and accelerated wear. In applications requiring large operating angles, constant velocity (CV) joints are often used to maintain a constant speed and accommodate greater angles. However, CV joints may introduce higher complexity and cost compared to U-joints.
3. Maintenance Requirements:
Drive shafts require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and reliability. This includes periodic inspection, lubrication of joints, and balancing if necessary. Failure to perform routine maintenance can lead to increased wear, vibrations, and potential driveline issues. Maintenance requirements should be considered in terms of time and resources when using drive shafts in various applications.
4. Noise and Vibration:
Drive shafts can generate noise and vibrations, especially at high speeds or when operating at certain resonant frequencies. Imbalances, misalignment, worn joints, or other factors can contribute to increased noise and vibrations. These vibrations may affect the comfort of vehicle occupants, contribute to component fatigue, and require additional measures such as dampers or vibration isolation systems to mitigate their effects.
5. Weight and Space Constraints:
Drive shafts add weight to the overall system, which can be a consideration in weight-sensitive applications, such as automotive or aerospace industries. Additionally, drive shafts require physical space for installation. In compact or tightly packaged equipment or vehicles, accommodating the necessary drive shaft length and clearances can be challenging, requiring careful design and integration considerations.
6. Cost Considerations:
Drive shafts, depending on their design, materials, and manufacturing processes, can involve significant costs. Customized or specialized drive shafts tailored to specific equipment requirements may incur higher expenses. Additionally, incorporating advanced joint configurations, such as CV joints, can add complexity and cost to the drive shaft system.
7. Inherent Power Loss:
Drive shafts transmit power from the driving source to the driven components, but they also introduce some inherent power loss due to friction, bending, and other factors. This power loss can reduce overall system efficiency, particularly in long drive shafts or applications with high torque requirements. It is important to consider power loss when determining the appropriate drive shaft design and specifications.
8. Limited Torque Capacity:
While drive shafts can handle a wide range of torque loads, there are limits to their torque capacity. Exceeding the maximum torque capacity of a drive shaft can lead to premature failure, resulting in downtime and potential damage to other driveline components. It is crucial to select a drive shaft with sufficient torque capacity for the intended application.
Despite these limitations and disadvantages, drive shafts remain a widely used and effective means of power transmission in various industries. Manufacturers continuously work to address these limitations through advancements in materials, design techniques, joint configurations, and balancing processes. By carefully considering the specific application requirements and potential drawbacks, engineers and designers can mitigate the limitations and maximize the benefits of drive shafts in their respective systems.

How do drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks?
Drive shafts play a significant role in enhancing the performance of automobiles and trucks. They contribute to various aspects of vehicle performance, including power delivery, traction, handling, and overall efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks:
1. Power Delivery:
Drive shafts are responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move forward. By efficiently transmitting power without significant losses, drive shafts ensure that the engine’s power is effectively utilized, resulting in improved acceleration and overall performance. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal power loss contribute to the vehicle’s ability to deliver power to the wheels efficiently.
2. Torque Transfer:
Drive shafts facilitate the transfer of torque from the engine to the wheels. Torque is the rotational force that drives the vehicle forward. High-quality drive shafts with proper torque conversion capabilities ensure that the torque generated by the engine is effectively transmitted to the wheels. This enhances the vehicle’s ability to accelerate quickly, tow heavy loads, and climb steep gradients, thereby improving overall performance.
3. Traction and Stability:
Drive shafts contribute to the traction and stability of automobiles and trucks. They transmit power to the wheels, allowing them to exert force on the road surface. This enables the vehicle to maintain traction, especially during acceleration or when driving on slippery or uneven terrain. The efficient power delivery through the drive shafts enhances the vehicle’s stability by ensuring balanced power distribution to all wheels, improving control and handling.
4. Handling and Maneuverability:
Drive shafts have an impact on the handling and maneuverability of vehicles. They help establish a direct connection between the engine and the wheels, allowing for precise control and responsive handling. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal play or backlash contribute to a more direct and immediate response to driver inputs, enhancing the vehicle’s agility and maneuverability.
5. Weight Reduction:
Drive shafts can contribute to weight reduction in automobiles and trucks. Lightweight drive shafts made from materials such as aluminum or carbon fiber-reinforced composites reduce the overall weight of the vehicle. The reduced weight improves the power-to-weight ratio, resulting in better acceleration, handling, and fuel efficiency. Additionally, lightweight drive shafts reduce the rotational mass, allowing the engine to rev up more quickly, further enhancing performance.
6. Mechanical Efficiency:
Efficient drive shafts minimize energy losses during power transmission. By incorporating features such as high-quality bearings, low-friction seals, and optimized lubrication, drive shafts reduce friction and minimize power losses due to internal resistance. This enhances the mechanical efficiency of the drivetrain system, allowing more power to reach the wheels and improving overall vehicle performance.
7. Performance Upgrades:
Drive shaft upgrades can be a popular performance enhancement for enthusiasts. Upgraded drive shafts, such as those made from stronger materials or with enhanced torque capacity, can handle higher power outputs from modified engines. These upgrades allow for increased performance, such as improved acceleration, higher top speeds, and better overall driving dynamics.
8. Compatibility with Performance Modifications:
Performance modifications, such as engine upgrades, increased power output, or changes to the drivetrain system, often require compatible drive shafts. Drive shafts designed to handle higher torque loads or adapt to modified drivetrain configurations ensure optimal performance and reliability. They enable the vehicle to effectively harness the increased power and torque, resulting in improved performance and responsiveness.
9. Durability and Reliability:
Robust and well-maintained drive shafts contribute to the durability and reliability of automobiles and trucks. They are designed to withstand the stresses and loads associated with power transmission. High-quality materials, appropriate balancing, and regular maintenance help ensure that drive shafts operate smoothly, minimizing the risk of failures or performance issues. Reliable drive shafts enhance the overall performance by providing consistent power delivery and minimizing downtime.
10. Compatibility with Advanced Technologies:
Drive shafts are evolving in tandem with advancements in vehicle technologies. They are increasingly being integrated with advanced systems such as hybrid powertrains, electric motors, and regenerative braking. Drive shafts designed to work seamlessly with these technologies maximize their efficiency and performance benefits, contributing to improved overall vehicle performance.
In summary, drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks by optimizing power delivery, facilitating torque transfer, improving traction and stability, enhancing handling and maneuverability, reducing weight, increasing mechanical efficiency,and enabling compatibility with performance upgrades and advanced technologies. They play a crucial role in ensuring efficient power transmission, responsive acceleration, precise handling, and overall improved performance of vehicles.
What is a drive shaft and how does it function in vehicles and machinery?
A drive shaft, also known as a propeller shaft or prop shaft, is a mechanical component that plays a critical role in transmitting rotational power from the engine to the wheels or other driven components in vehicles and machinery. It is commonly used in various types of vehicles, including cars, trucks, motorcycles, and agricultural or industrial machinery. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a drive shaft is and how it functions:
1. Definition and Construction: A drive shaft is a cylindrical metal tube that connects the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. It is typically made of steel or aluminum and consists of one or more tubular sections with universal joints (U-joints) at each end. These U-joints allow for angular movement and compensation of misalignment between the engine/transmission and the driven wheels or components.
2. Power Transmission: The primary function of a drive shaft is to transmit rotational power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. In vehicles, the drive shaft connects the transmission or gearbox output shaft to the differential, which then transfers power to the wheels. In machinery, the drive shaft transfers power from the engine or motor to various driven components such as pumps, generators, or other mechanical systems.
3. Torque and Speed: The drive shaft is responsible for transmitting both torque and rotational speed. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine or power source, while rotational speed is the number of revolutions per minute (RPM). The drive shaft must be capable of transmitting the required torque without excessive twisting or bending and maintaining the desired rotational speed for efficient operation of the driven components.
4. Flexible Coupling: The U-joints on the drive shaft provide a flexible coupling that allows for angular movement and compensation of misalignment between the engine/transmission and the driven wheels or components. As the suspension system of a vehicle moves or the machinery operates on uneven terrain, the drive shaft can adjust its length and angle to accommodate these movements, ensuring smooth power transmission and preventing damage to the drivetrain components.
5. Length and Balance: The length of the drive shaft is determined by the distance between the engine or power source and the driven wheels or components. It should be appropriately sized to ensure proper power transmission and avoid excessive vibrations or bending. Additionally, the drive shaft is carefully balanced to minimize vibrations and rotational imbalances, which can cause discomfort, reduce efficiency, and lead to premature wear of drivetrain components.
6. Safety Considerations: Drive shafts in vehicles and machinery require proper safety measures. In vehicles, drive shafts are often enclosed within a protective tube or housing to prevent contact with moving parts and reduce the risk of injury in the event of a malfunction or failure. Additionally, safety shields or guards are commonly installed around exposed drive shafts in machinery to protect operators from potential hazards associated with rotating components.
7. Maintenance and Inspection: Regular maintenance and inspection of drive shafts are essential to ensure their proper functioning and longevity. This includes checking for signs of wear, damage, or excessive play in the U-joints, inspecting the drive shaft for any cracks or deformations, and lubricating the U-joints as recommended by the manufacturer. Proper maintenance helps prevent failures, ensures optimal performance, and prolongs the service life of the drive shaft.
In summary, a drive shaft is a mechanical component that transmits rotational power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components in vehicles and machinery. It functions by providing a rigid connection between the engine/transmission and the driven wheels or components, while also allowing for angular movement and compensation of misalignment through the use of U-joints. The drive shaft plays a crucial role in power transmission, torque and speed delivery, flexible coupling, length and balance considerations, safety, and maintenance requirements. Its proper functioning is essential for the smooth and efficient operation of vehicles and machinery.


editor by CX 2024-01-29
China best CHINAMFG CHINAMFG Truck Parts Inter Axle Drive Shaft Az9557310625 Transmission Shaft
Product Description
Product Description
| Model NO. | Az9557310625 | Type | Rear Axles |
| Size | 25*5*10cm | Specification | 2kg |
| Quality | high-quality | Trademark | shibo |
| Origin | China | Production Capacity | 10000pieces/Months |
Detailed Photos
Packaging & Shipping
Company Profile
We adhere to the business policy of “quality first, service first, continuous improvement, cooperation and win-win”, and take “high quality, high standard” as the quality goal. We have an experienced and efficient team who understand and meet all your needs. Our products are of high quality, reasonable price, and considerate service. We have many partners and enjoy a good reputation all over the world.
We focus on integrity and commitment to make customers feel respected and efficient. We promise to do our best to provide the most professional and efficient services to global customers. Welcome new and old customers to contact us to establish sustainable business relationships and achieve CZPT cooperation!
Our Advantages
1.We supply parts to many truckexport companies as our competitive. Either original or OEM parts, we have lots of directly suppliers to choose. You could get HOWO/SHACMAN/FAW/XIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS.FENG spare parts bellow market price.
2.”One-stop foreign trade service”: Quotation–Preparation–Delivery.With 10+year experience,weProficient in parts business management process.
3.After getting your order, we will take pictures of every partsfor you. Even if you have 500 items.
4.With CZPT parts system,we can get the exact information according the chassis no and assembly nameplate , accurate rate reaches 95% .
After Sales Service
1,Reply your enquiry in 2 working hours.
2,100% delivery of all same quality.
3, Long lasting working life time.
4,Small order acceptable.
5,Timely delivery.
6,Excellent after-sale service.
7,Parts center build support for our dealers.
FAQ
1: Are you a manufacturer or trading company?
A: We are manufacturer.
Q2: What to do if I don’t know the part number?
A: If you give us the chassis number or the parts photos, we can provide the correct parts you needed.
Q3: Can you supply other spare parts?
A: Yes, of course. As you know, 1 truck has thousands of parts so that we can’t show all of them.Just tell us more details, we’ll find them for you.
Q4. What is your terms of payment?
A: T/T 30% as deposit, and 70% before delivery. We’ll show you the photos of the products and packages before you pay the balance.
Q5. How about your delivery time?
A: Generally, it will take 7 to 15 days after receiving your advance payment. The specific delivery time depends on the items and the quantity of your order.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Six Months |
|---|---|
| Condition: | Used |
| Color: | Black |
| Type: | Universal Joint |
| Material: | Iron |
| Material Quality: | Steel |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance?
Drive shafts employ various mechanisms to ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance. Efficient power transfer refers to the ability of the drive shaft to transmit rotational power from the source (such as an engine) to the driven components (such as wheels or machinery) with minimal energy loss. Balancing, on the other hand, involves minimizing vibrations and eliminating any uneven distribution of mass that can cause disturbances during operation. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts achieve both efficient power transfer and balance:
1. Material Selection:
The material selection for drive shafts is crucial for maintaining balance and ensuring efficient power transfer. Drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their strength, stiffness, and durability. These materials have excellent dimensional stability and can withstand the torque loads encountered during operation. By using high-quality materials, drive shafts can minimize deformation, flexing, and imbalances that could compromise power transmission and generate vibrations.
2. Design Considerations:
The design of the drive shaft plays a significant role in both power transfer efficiency and balance. Drive shafts are engineered to have appropriate dimensions, including diameter and wall thickness, to handle the anticipated torque loads without excessive deflection or vibration. The design also considers factors such as the length of the drive shaft, the number and type of joints (such as universal joints or constant velocity joints), and the use of balancing weights. By carefully designing the drive shaft, manufacturers can achieve optimal power transfer efficiency while minimizing the potential for imbalance-induced vibrations.
3. Balancing Techniques:
Balance is crucial for drive shafts as any imbalance can cause vibrations, noise, and accelerated wear. To maintain balance, drive shafts undergo various balancing techniques during the manufacturing process. Static and dynamic balancing methods are employed to ensure that the mass distribution along the drive shaft is uniform. Static balancing involves adding counterweights at specific locations to offset any weight imbalances. Dynamic balancing is performed by spinning the drive shaft at high speeds and measuring any vibrations. If imbalances are detected, additional adjustments are made to achieve a balanced state. These balancing techniques help minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation of the drive shaft.
4. Universal Joints and Constant Velocity Joints:
Drive shafts often incorporate universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints to accommodate misalignment and maintain balance during operation. U-joints are flexible joints that allow for angular movement between shafts. They are typically used in applications where the drive shaft operates at varying angles. CV joints, on the other hand, are designed to maintain a constant velocity of rotation and are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles. By incorporating these joints, drive shafts can compensate for misalignment, reduce stress on the shaft, and minimize vibrations that can negatively impact power transfer efficiency and balance.
5. Maintenance and Inspection:
Regular maintenance and inspection of drive shafts are essential for ensuring efficient power transfer and balance. Periodic checks for wear, damage, or misalignment can help identify any issues that may affect the drive shaft’s performance. Lubrication of the joints and proper tightening of fasteners are also critical for maintaining optimal operation. By adhering to recommended maintenance procedures, any imbalances or inefficiencies can be addressed promptly, ensuring continued efficient power transfer and balance.
In summary, drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance through careful material selection, thoughtful design considerations, balancing techniques, and the incorporation of flexible joints. By optimizing these factors, drive shafts can transmit rotational power smoothly and reliably, minimizing energy losses and vibrations that can impact performance and longevity.

Can drive shafts be customized for specific vehicle or equipment requirements?
Yes, drive shafts can be customized to meet specific vehicle or equipment requirements. Customization allows manufacturers to tailor the design, dimensions, materials, and other parameters of the drive shaft to ensure compatibility and optimal performance within a particular vehicle or equipment. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts can be customized:
1. Dimensional Customization:
Drive shafts can be customized to match the dimensional requirements of the vehicle or equipment. This includes adjusting the overall length, diameter, and spline configuration to ensure proper fitment and clearances within the specific application. By customizing the dimensions, the drive shaft can be seamlessly integrated into the driveline system without any interference or limitations.
2. Material Selection:
The choice of materials for drive shafts can be customized based on the specific requirements of the vehicle or equipment. Different materials, such as steel alloys, aluminum alloys, or specialized composites, can be selected to optimize strength, weight, and durability. The material selection can be tailored to meet the torque, speed, and operating conditions of the application, ensuring the drive shaft’s reliability and longevity.
3. Joint Configuration:
Drive shafts can be customized with different joint configurations to accommodate specific vehicle or equipment requirements. For example, universal joints (U-joints) may be suitable for applications with lower operating angles and moderate torque demands, while constant velocity (CV) joints are often used in applications requiring higher operating angles and smoother power transmission. The choice of joint configuration depends on factors such as operating angle, torque capacity, and desired performance characteristics.
4. Torque and Power Capacity:
Customization allows drive shafts to be designed with the appropriate torque and power capacity for the specific vehicle or equipment. Manufacturers can analyze the torque requirements, operating conditions, and safety margins of the application to determine the optimal torque rating and power capacity of the drive shaft. This ensures that the drive shaft can handle the required loads without experiencing premature failure or performance issues.
5. Balancing and Vibration Control:
Drive shafts can be customized with precision balancing and vibration control measures. Imbalances in the drive shaft can lead to vibrations, increased wear, and potential driveline issues. By employing dynamic balancing techniques during the manufacturing process, manufacturers can minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation. Additionally, vibration dampers or isolation systems can be integrated into the drive shaft design to further mitigate vibrations and enhance overall system performance.
6. Integration and Mounting Considerations:
Customization of drive shafts takes into account the integration and mounting requirements of the specific vehicle or equipment. Manufacturers work closely with the vehicle or equipment designers to ensure that the drive shaft fits seamlessly into the driveline system. This includes adapting the mounting points, interfaces, and clearances to ensure proper alignment and installation of the drive shaft within the vehicle or equipment.
7. Collaboration and Feedback:
Manufacturers often collaborate with vehicle manufacturers, OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers), or end-users to gather feedback and incorporate their specific requirements into the drive shaft customization process. By actively seeking input and feedback, manufacturers can address specific needs, optimize performance, and ensure compatibility with the vehicle or equipment. This collaborative approach enhances the customization process and results in drive shafts that meet the exact requirements of the application.
8. Compliance with Standards:
Customized drive shafts can be designed to comply with relevant industry standards and regulations. Compliance with standards, such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization) or specific industry standards, ensures that the customized drive shafts meet quality, safety, and performance requirements. Adhering to these standards provides assurance that the drive shafts are compatible and can be seamlessly integrated into the specific vehicle or equipment.
In summary, drive shafts can be customized to meet specific vehicle or equipment requirements through dimensional customization, material selection, joint configuration, torque and power capacity optimization, balancing and vibration control, integration and mounting considerations, collaboration with stakeholders, and compliance with industry standards. Customization allows drive shafts to be precisely tailored to the needs of the application, ensuring compatibility, reliability, and optimal performance.

Can you explain the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications?
Drive shafts come in various types, each designed to suit specific applications and requirements. The choice of drive shaft depends on factors such as the type of vehicle or equipment, power transmission needs, space limitations, and operating conditions. Here’s an explanation of the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications:
1. Solid Shaft:
A solid shaft, also known as a one-piece or solid-steel drive shaft, is a single, uninterrupted shaft that runs from the engine or power source to the driven components. It is a simple and robust design used in many applications. Solid shafts are commonly found in rear-wheel-drive vehicles, where they transmit power from the transmission to the rear axle. They are also used in industrial machinery, such as pumps, generators, and conveyors, where a straight and rigid power transmission is required.
2. Tubular Shaft:
Tubular shafts, also called hollow shafts, are drive shafts with a cylindrical tube-like structure. They are constructed with a hollow core and are typically lighter than solid shafts. Tubular shafts offer benefits such as reduced weight, improved torsional stiffness, and better damping of vibrations. They find applications in various vehicles, including cars, trucks, and motorcycles, as well as in industrial equipment and machinery. Tubular drive shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles, where they connect the transmission to the front wheels.
3. Constant Velocity (CV) Shaft:
Constant Velocity (CV) shafts are specifically designed to handle angular movement and maintain a constant velocity between the engine/transmission and the driven components. They incorporate CV joints at both ends, which allow flexibility and compensation for changes in angle. CV shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles, as well as in off-road vehicles and certain heavy machinery. The CV joints enable smooth power transmission even when the wheels are turned or the suspension moves, reducing vibrations and improving overall performance.
4. Slip Joint Shaft:
Slip joint shafts, also known as telescopic shafts, consist of two or more tubular sections that can slide in and out of each other. This design allows for length adjustment, accommodating changes in distance between the engine/transmission and the driven components. Slip joint shafts are commonly used in vehicles with long wheelbases or adjustable suspension systems, such as some trucks, buses, and recreational vehicles. By providing flexibility in length, slip joint shafts ensure a constant power transfer, even when the vehicle chassis experiences movement or changes in suspension geometry.
5. Double Cardan Shaft:
A double Cardan shaft, also referred to as a double universal joint shaft, is a type of drive shaft that incorporates two universal joints. This configuration helps to reduce vibrations and minimize the operating angles of the joints, resulting in smoother power transmission. Double Cardan shafts are commonly used in heavy-duty applications, such as trucks, off-road vehicles, and agricultural machinery. They are particularly suitable for applications with high torque requirements and large operating angles, providing enhanced durability and performance.
6. Composite Shaft:
Composite shafts are made from composite materials such as carbon fiber or fiberglass, offering advantages such as reduced weight, improved strength, and resistance to corrosion. Composite drive shafts are increasingly being used in high-performance vehicles, sports cars, and racing applications, where weight reduction and enhanced power-to-weight ratio are critical. The composite construction allows for precise tuning of stiffness and damping characteristics, resulting in improved vehicle dynamics and drivetrain efficiency.
7. PTO Shaft:
Power Take-Off (PTO) shafts are specialized drive shafts used in agricultural machinery and certain industrial equipment. They are designed to transfer power from the engine or power source to various attachments, such as mowers, balers, or pumps. PTO shafts typically have a splined connection at one end to connect to the power source and a universal joint at the other end to accommodate angular movement. They are characterized by their ability to transmit high torque levels and their compatibility with a range of driven implements.
8. Marine Shaft:
Marine shafts, also known as propeller shafts or tail shafts, are specifically designed for marine vessels. They transmit power from the engine to the propeller, enabling propulsion. Marine shafts are usually long and operate in a harsh environment, exposed to water, corrosion, and high torque loads. They are typically made of stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials and are designed to withstand the challenging conditions encountered in marine applications.
It’simportant to note that the specific applications of drive shafts may vary depending on the vehicle or equipment manufacturer, as well as the specific design and engineering requirements. The examples provided above highlight common applications for each type of drive shaft, but there may be additional variations and specialized designs based on specific industry needs and technological advancements.


editor by CX 2024-01-25
China best Front Drive Axle Half Shaft for CZPT Truck Parts HD90009420019/HD90009420020/81.36402.6328/HD9100942006
Product Description
Original Factory Front Drive Axle Shaft Half Shaft For CZPT Truck Parts HDHD81.36402.6328 HD9100942006
Detailed Photos
Product advantages & features
(1) Accessory products of the truck, the product quality is stable and reliable.
(2) Forged with 42CrMo material and heat treated and tempered for 32 degrees, so that the half shaft has stronger toughness and is not easy to break and bend.
(3) After the bend is adjusted, the sandblasting process is carried out to make the appearance of the half shaft more fine.
(4) Processed in the machining center, ensure that the products have rigorous dimensional coordinates to ensure 100% qualified rate of products.
(5) Products are inspected 1 by 1 and delivered out of the warehouse, with unified laser identification to ensure product traceability.
(6) Various sizes of axle shafts can be customized to meet customer needs.
(7) The unified brand carton, inner bag and integral foam packaging, which is strong and beautiful.
Factory Show
More Products
| Truck Model | Sinotruk, Shacman, CZPT Auman, CZPT Xihu (West Lake) Dis., Xihu (West Lake) Dis.feng, Xihu (West Lake) Dis.feng Liuqi Balong, North BENZ( BEIBEN), C&C, JAC, etc. | |
| Product catalogue | Axle | Wheel Assembly |
| Differential Assembly | ||
| Main Reducer Assembly | ||
| Inner Ring Gear& Bracket | ||
| Basin Angle Gear/ Bevel Gear | ||
| Axle Shaft/ Half Shaft & Through Shaft | ||
| Axle Housing& Axle Assembly | ||
| Steering knuckle & Front Axle | ||
| Gear | ||
| Brake Drum& Wheel Hub | ||
| Flange | ||
| Bearing | ||
| Main Reducer Housing | ||
| Oil Seal Seat | ||
| Nut& Shim Series | ||
| Brake Backing Plate | ||
| Chassis Support Products | Leaf Spring Bracket | |
| Drop Arm Series | ||
| Bracket Series | ||
| Leaf Spring Shackle Series | ||
| Balanced Suspension Series | Balance Shaft Assembly | |
| Balance Shaft Housing | ||
| Axle Spring Seat | ||
| Thrust Rod | ||
| Balance Shaft Parts | ||
| Shock Absorber Series | Shock Absorber | |
| Shock Absorbing Airbag | ||
| Steering System | Power Steering Pump | |
| Power Steering Gear | ||
| Rubber Products | Oil Seal | |
| Rubber Support | ||
| Thrust Rod Rubber Core | ||
| Truck Belt | ||
| Engine support | ||
| Other | ||
| Clutch Series | Clutch Pressure Plate | |
| Clutch Disc | ||
| Flywheel Assembly | ||
| Flywheel Ring Gear | ||
| Adjusting Arm Series | ||
Packaging & Shipping
Function
The half shaft of a car is the transmission shaft. The car needs to turn after driving. The rotation of wheels on both sides is different. One side is faster and the other side is slower, which requires a differential on the transmission shaft. The differential is a device that makes the wheels on both sides rotate at different speeds. The half shaft is connected to the differential and then to the wheels.
The ends of each half axle are respectively connected with the wheels on its side and the differential. The torque and speed distributed by the differential are transmitted to the wheels to drive the wheels to rotate. The speed transmitted from the half shaft of general construction machinery such as loaders and cranes needs to be further decelerated by the wheel reducer to increase the torque and make the wheels have stronger driving force. The wheel reducer is the planetary gear reducer.
Honor Certificate
FAQ
Q1. Are you a factory or trading company?
We are a factory integrating research, development, production and sales.
Q2. What are the advantages of your products?
We support product customization to meet customer needs for special products. We can strictly control the products from raw materials to production, processing, product quality inspection, delivery, packaging, etc., and provide customers with high-end products and the most advantageous prices.
Q3. How about products price?
We are a factory, all products are direct sale at factory price. For the same price, we will provide the best quality; for the same quality, we have the most advantageous price.
Q4. What is your terms of packing?
We have branded packaging and neutral packaging, and we can also do what you want with authorization. This is flexible.
Q5. How to guarantee your after-sales service?
Strict inspection during production, Strictly check the products before shipment to ensure our packaging in good condition. Track and receive feedback from customer regularly. Our products warranty is 365 days.
Each product provides quality assurance service. If there is a problem with the product within the warranty period, the customer can negotiate with us in detail about the related claims, and we will do our best to satisfy the customer.
Q6. How can I accurately buy the products I need?
We need accurate product number, If you can’t provide product number, you can send us your product picture, or tell us your truck model, engine name plate, and so on. we will
determine exactly what you need products.
Q7. Do you accept third party inspection?
Yes.we do
Q8. How about your delivery time?
Generally, it will take 3 to 10 days after receiving your advance payment. The specific delivery time depends on the items and the quantity of your order.
Q9. What are your brand agency conditions and advantages?
After we CZPT an agent in 1 city, we will not CZPT a second company to protect the agent’s brand advantage and price advantage. And we will help the agent develop customers and solve all kinds of difficult and miscellaneous problems about products.
Q10. What is your terms of payment?
By TT or LC. We’ll show you the photos of the products and packages before you pay the balance.
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated |
|---|
| After-sales Service: | Support |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Application: | Shacman Truck |
| Samples: |
US$ 31/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Are there any limitations or disadvantages associated with drive shafts?
While drive shafts are widely used and offer several advantages, they also have certain limitations and disadvantages that should be considered. Here’s a detailed explanation of the limitations and disadvantages associated with drive shafts:
1. Length and Misalignment Constraints:
Drive shafts have a maximum practical length due to factors such as material strength, weight considerations, and the need to maintain rigidity and minimize vibrations. Longer drive shafts can be prone to increased bending and torsional deflection, leading to reduced efficiency and potential driveline vibrations. Additionally, drive shafts require proper alignment between the driving and driven components. Misalignment can cause increased wear, vibrations, and premature failure of the drive shaft or its associated components.
2. Limited Operating Angles:
Drive shafts, especially those using U-joints, have limitations on operating angles. U-joints are typically designed to operate within specific angular ranges, and operating beyond these limits can result in reduced efficiency, increased vibrations, and accelerated wear. In applications requiring large operating angles, constant velocity (CV) joints are often used to maintain a constant speed and accommodate greater angles. However, CV joints may introduce higher complexity and cost compared to U-joints.
3. Maintenance Requirements:
Drive shafts require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and reliability. This includes periodic inspection, lubrication of joints, and balancing if necessary. Failure to perform routine maintenance can lead to increased wear, vibrations, and potential driveline issues. Maintenance requirements should be considered in terms of time and resources when using drive shafts in various applications.
4. Noise and Vibration:
Drive shafts can generate noise and vibrations, especially at high speeds or when operating at certain resonant frequencies. Imbalances, misalignment, worn joints, or other factors can contribute to increased noise and vibrations. These vibrations may affect the comfort of vehicle occupants, contribute to component fatigue, and require additional measures such as dampers or vibration isolation systems to mitigate their effects.
5. Weight and Space Constraints:
Drive shafts add weight to the overall system, which can be a consideration in weight-sensitive applications, such as automotive or aerospace industries. Additionally, drive shafts require physical space for installation. In compact or tightly packaged equipment or vehicles, accommodating the necessary drive shaft length and clearances can be challenging, requiring careful design and integration considerations.
6. Cost Considerations:
Drive shafts, depending on their design, materials, and manufacturing processes, can involve significant costs. Customized or specialized drive shafts tailored to specific equipment requirements may incur higher expenses. Additionally, incorporating advanced joint configurations, such as CV joints, can add complexity and cost to the drive shaft system.
7. Inherent Power Loss:
Drive shafts transmit power from the driving source to the driven components, but they also introduce some inherent power loss due to friction, bending, and other factors. This power loss can reduce overall system efficiency, particularly in long drive shafts or applications with high torque requirements. It is important to consider power loss when determining the appropriate drive shaft design and specifications.
8. Limited Torque Capacity:
While drive shafts can handle a wide range of torque loads, there are limits to their torque capacity. Exceeding the maximum torque capacity of a drive shaft can lead to premature failure, resulting in downtime and potential damage to other driveline components. It is crucial to select a drive shaft with sufficient torque capacity for the intended application.
Despite these limitations and disadvantages, drive shafts remain a widely used and effective means of power transmission in various industries. Manufacturers continuously work to address these limitations through advancements in materials, design techniques, joint configurations, and balancing processes. By carefully considering the specific application requirements and potential drawbacks, engineers and designers can mitigate the limitations and maximize the benefits of drive shafts in their respective systems.

How do drive shafts handle variations in load and vibration during operation?
Drive shafts are designed to handle variations in load and vibration during operation by employing various mechanisms and features. These mechanisms help ensure smooth power transmission, minimize vibrations, and maintain the structural integrity of the drive shaft. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts handle load and vibration variations:
1. Material Selection and Design:
Drive shafts are typically made from materials with high strength and stiffness, such as steel alloys or composite materials. The material selection and design take into account the anticipated loads and operating conditions of the application. By using appropriate materials and optimizing the design, drive shafts can withstand the expected variations in load without experiencing excessive deflection or deformation.
2. Torque Capacity:
Drive shafts are designed with a specific torque capacity that corresponds to the expected loads. The torque capacity takes into account factors such as the power output of the driving source and the torque requirements of the driven components. By selecting a drive shaft with sufficient torque capacity, variations in load can be accommodated without exceeding the drive shaft’s limits and risking failure or damage.
3. Dynamic Balancing:
During the manufacturing process, drive shafts can undergo dynamic balancing. Imbalances in the drive shaft can result in vibrations during operation. Through the balancing process, weights are strategically added or removed to ensure that the drive shaft spins evenly and minimizes vibrations. Dynamic balancing helps to mitigate the effects of load variations and reduces the potential for excessive vibrations in the drive shaft.
4. Dampers and Vibration Control:
Drive shafts can incorporate dampers or vibration control mechanisms to further minimize vibrations. These devices are typically designed to absorb or dissipate vibrations that may arise from load variations or other factors. Dampers can be in the form of torsional dampers, rubber isolators, or other vibration-absorbing elements strategically placed along the drive shaft. By managing and attenuating vibrations, drive shafts ensure smooth operation and enhance overall system performance.
5. CV Joints:
Constant Velocity (CV) joints are often used in drive shafts to accommodate variations in operating angles and to maintain a constant speed. CV joints allow the drive shaft to transmit power even when the driving and driven components are at different angles. By accommodating variations in operating angles, CV joints help minimize the impact of load variations and reduce potential vibrations that may arise from changes in the driveline geometry.
6. Lubrication and Maintenance:
Proper lubrication and regular maintenance are essential for drive shafts to handle load and vibration variations effectively. Lubrication helps reduce friction between moving parts, minimizing wear and heat generation. Regular maintenance, including inspection and lubrication of joints, ensures that the drive shaft remains in optimal condition, reducing the risk of failure or performance degradation due to load variations.
7. Structural Rigidity:
Drive shafts are designed to have sufficient structural rigidity to resist bending and torsional forces. This rigidity helps maintain the integrity of the drive shaft when subjected to load variations. By minimizing deflection and maintaining structural integrity, the drive shaft can effectively transmit power and handle variations in load without compromising performance or introducing excessive vibrations.
8. Control Systems and Feedback:
In some applications, drive shafts may be equipped with control systems that actively monitor and adjust parameters such as torque, speed, and vibration. These control systems use sensors and feedback mechanisms to detect variations in load or vibrations and make real-time adjustments to optimize performance. By actively managing load variations and vibrations, drive shafts can adapt to changing operating conditions and maintain smooth operation.
In summary, drive shafts handle variations in load and vibration during operation through careful material selection and design, torque capacity considerations, dynamic balancing, integration of dampers and vibration control mechanisms, utilization of CV joints, proper lubrication and maintenance, structural rigidity, and, in some cases, control systems and feedback mechanisms. By incorporating these features and mechanisms, drive shafts ensure reliable and efficient power transmission while minimizing the impact of load variations and vibrations on overall system performance.

How do drive shafts handle variations in length and torque requirements?
Drive shafts are designed to handle variations in length and torque requirements in order to efficiently transmit rotational power. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts address these variations:
Length Variations:
Drive shafts are available in different lengths to accommodate varying distances between the engine or power source and the driven components. They can be custom-made or purchased in standardized lengths, depending on the specific application. In situations where the distance between the engine and the driven components is longer, multiple drive shafts with appropriate couplings or universal joints can be used to bridge the gap. These additional drive shafts effectively extend the overall length of the power transmission system.
Additionally, some drive shafts are designed with telescopic sections. These sections can be extended or retracted, allowing for adjustments in length to accommodate different vehicle configurations or dynamic movements. Telescopic drive shafts are commonly used in applications where the distance between the engine and the driven components may change, such as in certain types of trucks, buses, and off-road vehicles.
Torque Requirements:
Drive shafts are engineered to handle varying torque requirements based on the power output of the engine or power source and the demands of the driven components. The torque transmitted through the drive shaft depends on factors such as the engine power, load conditions, and the resistance encountered by the driven components.
Manufacturers consider torque requirements when selecting the appropriate materials and dimensions for drive shafts. Drive shafts are typically made from high-strength materials, such as steel or aluminum alloys, to withstand the torque loads without deformation or failure. The diameter, wall thickness, and design of the drive shaft are carefully calculated to ensure it can handle the expected torque without excessive deflection or vibration.
In applications with high torque demands, such as heavy-duty trucks, industrial machinery, or performance vehicles, drive shafts may have additional reinforcements. These reinforcements can include thicker walls, cross-sectional shapes optimized for strength, or composite materials with superior torque-handling capabilities.
Furthermore, drive shafts often incorporate flexible joints, such as universal joints or constant velocity (CV) joints. These joints allow for angular misalignment and compensate for variations in the operating angles between the engine, transmission, and driven components. They also help absorb vibrations and shocks, reducing stress on the drive shaft and enhancing its torque-handling capacity.
In summary, drive shafts handle variations in length and torque requirements through customizable lengths, telescopic sections, appropriate materials and dimensions, and the inclusion of flexible joints. By carefully considering these factors, drive shafts can efficiently and reliably transmit power while accommodating the specific needs of different applications.


editor by CX 2023-10-02
China Good quality Gjf Auto Spare Parts CV Axle Drive Shaft for CZPT Patrol Y60 1987- C-Ni085-8h
Product Description
Product Description
1.We are manufacturer of cv drive shaft,cv axle, cv joint and cv boot, we have more than 20-years experience in producing and selling auto parts.
2.We have strict quality control, the quality of our products is very good.
3.We are professional in different market around the world.
4.The reviews our customers given us are very positive, we have confidence in our products.
5.OEM/ODM is available, meet your requirements well.
6.Large warehouse, huge stocks!!! friendly for those customers who want some quantity.
7.Ship products out very fastly, we have stock.
| Product Name | Drive shaft | Material | 42CrMo alloy steel |
| Car fitment | Nissan | 12 months | |
| Model | PATROL GR IV Platform/Chassis (Y60) | ZHangZhoug, China | |
| year | 1994-2000 | 4 PCS | |
| OE number | C-NI085-8H | 1-7 days | |
| Yes | Brand | GJF | |
| Packing size | 1.12*0.26*0.26 | L/C,T/T,western Union,Cash,PayPal | |
| Sample service | Depends on the situation of stock | Weight | About 3.7kg-14.5kg |
Detailed Photos
Customer Review
Packaging & Shipping
FAQ
| After-sales Service: | 12 Months |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Axle Number: | 1 |
| Application: | Car |
| Certification: | ASTM, CE, DIN, ISO |
| Material: | Alloy |
| Samples: |
US$ 42/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What factors should be considered when selecting the right drive shaft for an application?
When selecting the right drive shaft for an application, several factors need to be considered. The choice of drive shaft plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient and reliable power transmission. Here are the key factors to consider:
1. Power and Torque Requirements:
The power and torque requirements of the application are essential considerations. It is crucial to determine the maximum torque that the drive shaft will need to transmit without failure or excessive deflection. This includes evaluating the power output of the engine or power source, as well as the torque demands of the driven components. Selecting a drive shaft with the appropriate diameter, material strength, and design is essential to ensure it can handle the expected torque levels without compromising performance or safety.
2. Operating Speed:
The operating speed of the drive shaft is another critical factor. The rotational speed affects the dynamic behavior of the drive shaft, including the potential for vibration, resonance, and critical speed limitations. It is important to choose a drive shaft that can operate within the desired speed range without encountering excessive vibrations or compromising the structural integrity. Factors such as the material properties, balance, and critical speed analysis should be considered to ensure the drive shaft can handle the required operating speed effectively.
3. Length and Alignment:
The length and alignment requirements of the application must be considered when selecting a drive shaft. The distance between the engine or power source and the driven components determines the required length of the drive shaft. In situations where there are significant variations in length or operating angles, telescopic drive shafts or multiple drive shafts with appropriate couplings or universal joints may be necessary. Proper alignment of the drive shaft is crucial to minimize vibrations, reduce wear and tear, and ensure efficient power transmission.
4. Space Limitations:
The available space within the application is an important factor to consider. The drive shaft must fit within the allocated space without interfering with other components or structures. It is essential to consider the overall dimensions of the drive shaft, including length, diameter, and any additional components such as joints or couplings. In some cases, custom or compact drive shaft designs may be required to accommodate space limitations while maintaining adequate power transmission capabilities.
5. Environmental Conditions:
The environmental conditions in which the drive shaft will operate should be evaluated. Factors such as temperature, humidity, corrosive agents, and exposure to contaminants can impact the performance and lifespan of the drive shaft. It is important to select materials and coatings that can withstand the specific environmental conditions to prevent corrosion, degradation, or premature failure of the drive shaft. Special considerations may be necessary for applications exposed to extreme temperatures, water, chemicals, or abrasive substances.
6. Application Type and Industry:
The specific application type and industry requirements play a significant role in drive shaft selection. Different industries, such as automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery, agriculture, or marine, have unique demands that need to be addressed. Understanding the specific needs and operating conditions of the application is crucial in determining the appropriate drive shaft design, materials, and performance characteristics. Compliance with industry standards and regulations may also be a consideration in certain applications.
7. Maintenance and Serviceability:
The ease of maintenance and serviceability should be taken into account. Some drive shaft designs may require periodic inspection, lubrication, or replacement of components. Considering the accessibility of the drive shaft and associated maintenance requirements can help minimize downtime and ensure long-term reliability. Easy disassembly and reassembly of the drive shaft can also be beneficial for repair or component replacement.
By carefully considering these factors, one can select the right drive shaft for an application that meets the power transmission needs, operating conditions, and durability requirements, ultimately ensuring optimal performance and reliability.

How do drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks?
Drive shafts play a significant role in enhancing the performance of automobiles and trucks. They contribute to various aspects of vehicle performance, including power delivery, traction, handling, and overall efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks:
1. Power Delivery: Drive shafts are responsible for transmitting power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move forward. By efficiently transferring power without significant losses, drive shafts ensure that the engine’s power is effectively utilized, resulting in improved acceleration and overall performance. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal power loss contribute to the vehicle’s ability to deliver power to the wheels efficiently.
2. Torque Transfer: Drive shafts facilitate the transfer of torque from the engine to the wheels. Torque is the rotational force that drives the vehicle forward. High-quality drive shafts with proper torque conversion capabilities ensure that the torque generated by the engine is effectively transmitted to the wheels. This enhances the vehicle’s ability to accelerate quickly, tow heavy loads, and climb steep gradients, thereby improving overall performance.
3. Traction and Stability: Drive shafts contribute to the traction and stability of automobiles and trucks. They transmit power to the wheels, allowing them to exert force on the road surface. This enables the vehicle to maintain traction, especially during acceleration or when driving on slippery or uneven terrain. The efficient power delivery through the drive shafts enhances the vehicle’s stability by ensuring balanced power distribution to all wheels, improving control and handling.
4. Handling and Maneuverability: Drive shafts have an impact on the handling and maneuverability of vehicles. They help establish a direct connection between the engine and the wheels, allowing for precise control and responsive handling. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal play or backlash contribute to a more direct and immediate response to driver inputs, enhancing the vehicle’s agility and maneuverability.
5. Weight Reduction: Drive shafts can contribute to weight reduction in automobiles and trucks. Lightweight drive shafts made from materials such as aluminum or carbon fiber-reinforced composites reduce the overall weight of the vehicle. The reduced weight improves the power-to-weight ratio, resulting in better acceleration, handling, and fuel efficiency. Additionally, lightweight drive shafts reduce the rotational mass, allowing the engine to rev up more quickly, further enhancing performance.
6. Mechanical Efficiency: Efficient drive shafts minimize energy losses during power transmission. By incorporating features such as high-quality bearings, low-friction seals, and optimized lubrication, drive shafts reduce friction and minimize power losses due to internal resistance. This enhances the mechanical efficiency of the drivetrain system, allowing more power to reach the wheels and improving overall vehicle performance.
7. Performance Upgrades: Drive shaft upgrades can be popular performance enhancements for enthusiasts. Upgraded drive shafts, such as those made from stronger materials or with enhanced torque capacity, can handle higher power outputs from modified engines. These upgrades allow for increased performance, such as improved acceleration, higher top speeds, and better overall driving dynamics.
8. Compatibility with Performance Modifications: Performance modifications, such as engine upgrades, increased power output, or changes to the drivetrain system, often require compatible drive shafts. Drive shafts designed to handle higher torque loads or adapt to modified drivetrain configurations ensure optimal performance and reliability. They enable the vehicle to effectively harness the increased power and torque, resulting in improved performance and responsiveness.
9. Durability and Reliability: Robust and well-maintained drive shafts contribute to the durability and reliability of automobiles and trucks. They are designed to withstand the stresses and loads associated with power transmission. High-quality materials, appropriate balancing, and regular maintenance help ensure that drive shafts operate smoothly, minimizing the risk of failures or performance issues. Reliable drive shafts enhance the overall performance by providing consistent power delivery and minimizing downtime.
10. Compatibility with Advanced Technologies: Drive shafts are evolving in tandem with advancements in vehicle technologies. They are increasingly being integrated with advanced systems such as hybrid powertrains, electric motors, and regenerative braking. Drive shafts designed to work seamlessly with these technologies maximize their efficiency and performance benefits, contributing to improved overall vehicle performance.
In summary, drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks by optimizing power delivery, facilitating torque transfer, improving traction and stability, enhancing handling and maneuverability, reducing weight, increasing mechanical efficiency, enabling compatibility with performance upgrades and advanced technologies, and ensuring durability and reliability. They play a crucial role in ensuring efficient power transmission, responsive acceleration, precise handling, and overall improved performance of vehicles.

Can you explain the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications?
Drive shafts come in various types, each designed to suit specific applications and requirements. The choice of drive shaft depends on factors such as the type of vehicle or equipment, power transmission needs, space limitations, and operating conditions. Here’s an explanation of the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications:
1. Solid Shaft:
A solid shaft, also known as a one-piece or solid-steel drive shaft, is a single, uninterrupted shaft that runs from the engine or power source to the driven components. It is a simple and robust design used in many applications. Solid shafts are commonly found in rear-wheel-drive vehicles, where they transmit power from the transmission to the rear axle. They are also used in industrial machinery, such as pumps, generators, and conveyors, where a straight and rigid power transmission is required.
2. Tubular Shaft:
Tubular shafts, also called hollow shafts, are drive shafts with a cylindrical tube-like structure. They are constructed with a hollow core and are typically lighter than solid shafts. Tubular shafts offer benefits such as reduced weight, improved torsional stiffness, and better damping of vibrations. They find applications in various vehicles, including cars, trucks, and motorcycles, as well as in industrial equipment and machinery. Tubular drive shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles, where they connect the transmission to the front wheels.
3. Constant Velocity (CV) Shaft:
Constant Velocity (CV) shafts are specifically designed to handle angular movement and maintain a constant velocity between the engine/transmission and the driven components. They incorporate CV joints at both ends, which allow flexibility and compensation for changes in angle. CV shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles, as well as in off-road vehicles and certain heavy machinery. The CV joints enable smooth power transmission even when the wheels are turned or the suspension moves, reducing vibrations and improving overall performance.
4. Slip Joint Shaft:
Slip joint shafts, also known as telescopic shafts, consist of two or more tubular sections that can slide in and out of each other. This design allows for length adjustment, accommodating changes in distance between the engine/transmission and the driven components. Slip joint shafts are commonly used in vehicles with long wheelbases or adjustable suspension systems, such as some trucks, buses, and recreational vehicles. By providing flexibility in length, slip joint shafts ensure a constant power transfer, even when the vehicle chassis experiences movement or changes in suspension geometry.
5. Double Cardan Shaft:
A double Cardan shaft, also referred to as a double universal joint shaft, is a type of drive shaft that incorporates two universal joints. This configuration helps to reduce vibrations and minimize the operating angles of the joints, resulting in smoother power transmission. Double Cardan shafts are commonly used in heavy-duty applications, such as trucks, off-road vehicles, and agricultural machinery. They are particularly suitable for applications with high torque requirements and large operating angles, providing enhanced durability and performance.
6. Composite Shaft:
Composite shafts are made from composite materials such as carbon fiber or fiberglass, offering advantages such as reduced weight, improved strength, and resistance to corrosion. Composite drive shafts are increasingly being used in high-performance vehicles, sports cars, and racing applications, where weight reduction and enhanced power-to-weight ratio are critical. The composite construction allows for precise tuning of stiffness and damping characteristics, resulting in improved vehicle dynamics and drivetrain efficiency.
7. PTO Shaft:
Power Take-Off (PTO) shafts are specialized drive shafts used in agricultural machinery and certain industrial equipment. They are designed to transfer power from the engine or power source to various attachments, such as mowers, balers, or pumps. PTO shafts typically have a splined connection at one end to connect to the power source and a universal joint at the other end to accommodate angular movement. They are characterized by their ability to transmit high torque levels and their compatibility with a range of driven implements.
8. Marine Shaft:
Marine shafts, also known as propeller shafts or tail shafts, are specifically designed for marine vessels. They transmit power from the engine to the propeller, enabling propulsion. Marine shafts are usually long and operate in a harsh environment, exposed to water, corrosion, and high torque loads. They are typically made of stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials and are designed to withstand the challenging conditions encountered in marine applications.
It’simportant to note that the specific applications of drive shafts may vary depending on the vehicle or equipment manufacturer, as well as the specific design and engineering requirements. The examples provided above highlight common applications for each type of drive shaft, but there may be additional variations and specialized designs based on specific industry needs and technological advancements.


editor by CX 2023-09-28
China manufacturer Front Drive Axle Half Shaft for CZPT Truck Parts HD90009420019/HD90009420020/81.36402.6328/HD9100942006
Product Description
Original Factory Front Drive Axle Shaft Half Shaft For CZPT Truck Parts HDHD81.36402.6328 HD9100942006
Detailed Photos
Product advantages & features
(1) Accessory products of the truck, the product quality is stable and reliable.
(2) Forged with 42CrMo material and heat treated and tempered for 32 degrees, so that the half shaft has stronger toughness and is not easy to break and bend.
(3) After the bend is adjusted, the sandblasting process is carried out to make the appearance of the half shaft more fine.
(4) Processed in the machining center, ensure that the products have rigorous dimensional coordinates to ensure 100% qualified rate of products.
(5) Products are inspected 1 by 1 and delivered out of the warehouse, with unified laser identification to ensure product traceability.
(6) Various sizes of axle shafts can be customized to meet customer needs.
(7) The unified brand carton, inner bag and integral foam packaging, which is strong and beautiful.
Factory Show
More Products
| Truck Model | Sinotruk, Shacman, CZPT Auman, CZPT Xihu (West Lake) Dis., Xihu (West Lake) Dis.feng, Xihu (West Lake) Dis.feng Liuqi Balong, North BENZ( BEIBEN), C&C, JAC, etc. | |
| Product catalogue | Axle | Wheel Assembly |
| Differential Assembly | ||
| Main Reducer Assembly | ||
| Inner Ring Gear& Bracket | ||
| Basin Angle Gear/ Bevel Gear | ||
| Axle Shaft/ Half Shaft & Through Shaft | ||
| Axle Housing& Axle Assembly | ||
| Steering knuckle & Front Axle | ||
| Gear | ||
| Brake Drum& Wheel Hub | ||
| Flange | ||
| Bearing | ||
| Main Reducer Housing | ||
| Oil Seal Seat | ||
| Nut& Shim Series | ||
| Brake Backing Plate | ||
| Chassis Support Products | Leaf Spring Bracket | |
| Drop Arm Series | ||
| Bracket Series | ||
| Leaf Spring Shackle Series | ||
| Balanced Suspension Series | Balance Shaft Assembly | |
| Balance Shaft Housing | ||
| Axle Spring Seat | ||
| Thrust Rod | ||
| Balance Shaft Parts | ||
| Shock Absorber Series | Shock Absorber | |
| Shock Absorbing Airbag | ||
| Steering System | Power Steering Pump | |
| Power Steering Gear | ||
| Rubber Products | Oil Seal | |
| Rubber Support | ||
| Thrust Rod Rubber Core | ||
| Truck Belt | ||
| Engine support | ||
| Other | ||
| Clutch Series | Clutch Pressure Plate | |
| Clutch Disc | ||
| Flywheel Assembly | ||
| Flywheel Ring Gear | ||
| Adjusting Arm Series | ||
Packaging & Shipping
Function
The half shaft of a car is the transmission shaft. The car needs to turn after driving. The rotation of wheels on both sides is different. One side is faster and the other side is slower, which requires a differential on the transmission shaft. The differential is a device that makes the wheels on both sides rotate at different speeds. The half shaft is connected to the differential and then to the wheels.
The ends of each half axle are respectively connected with the wheels on its side and the differential. The torque and speed distributed by the differential are transmitted to the wheels to drive the wheels to rotate. The speed transmitted from the half shaft of general construction machinery such as loaders and cranes needs to be further decelerated by the wheel reducer to increase the torque and make the wheels have stronger driving force. The wheel reducer is the planetary gear reducer.
Honor Certificate
FAQ
Q1. Are you a factory or trading company?
We are a factory integrating research, development, production and sales.
Q2. What are the advantages of your products?
We support product customization to meet customer needs for special products. We can strictly control the products from raw materials to production, processing, product quality inspection, delivery, packaging, etc., and provide customers with high-end products and the most advantageous prices.
Q3. How about products price?
We are a factory, all products are direct sale at factory price. For the same price, we will provide the best quality; for the same quality, we have the most advantageous price.
Q4. What is your terms of packing?
We have branded packaging and neutral packaging, and we can also do what you want with authorization. This is flexible.
Q5. How to guarantee your after-sales service?
Strict inspection during production, Strictly check the products before shipment to ensure our packaging in good condition. Track and receive feedback from customer regularly. Our products warranty is 365 days.
Each product provides quality assurance service. If there is a problem with the product within the warranty period, the customer can negotiate with us in detail about the related claims, and we will do our best to satisfy the customer.
Q6. How can I accurately buy the products I need?
We need accurate product number, If you can’t provide product number, you can send us your product picture, or tell us your truck model, engine name plate, and so on. we will
determine exactly what you need products.
Q7. Do you accept third party inspection?
Yes.we do
Q8. How about your delivery time?
Generally, it will take 3 to 10 days after receiving your advance payment. The specific delivery time depends on the items and the quantity of your order.
Q9. What are your brand agency conditions and advantages?
After we CZPT an agent in 1 city, we will not CZPT a second company to protect the agent’s brand advantage and price advantage. And we will help the agent develop customers and solve all kinds of difficult and miscellaneous problems about products.
Q10. What is your terms of payment?
By TT or LC. We’ll show you the photos of the products and packages before you pay the balance.
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated |
|---|
| After-sales Service: | Support |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Application: | Shacman Truck |
| Samples: |
US$ 31/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
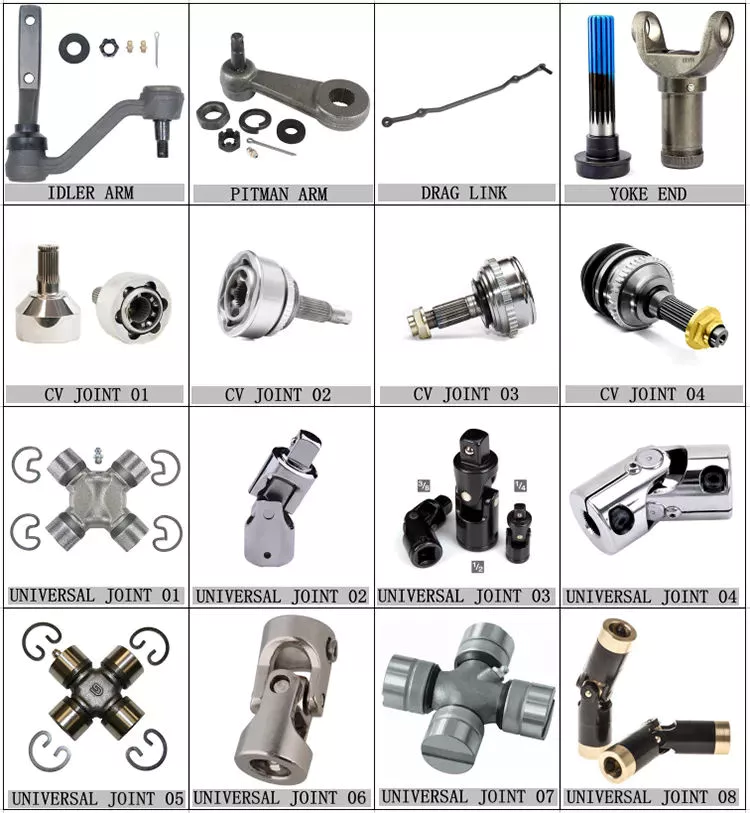

How do drive shafts handle variations in speed and torque during operation?
Drive shafts are designed to handle variations in speed and torque during operation by employing specific mechanisms and configurations. These mechanisms allow the drive shafts to accommodate the changing demands of power transmission while maintaining smooth and efficient operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts handle variations in speed and torque:
1. Flexible Couplings:
Drive shafts often incorporate flexible couplings, such as universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints, to handle variations in speed and torque. These couplings provide flexibility and allow the drive shaft to transmit power even when the driving and driven components are not perfectly aligned. U-joints consist of two yokes connected by a cross-shaped bearing, allowing for angular movement between the drive shaft sections. This flexibility accommodates variations in speed and torque and compensates for misalignment. CV joints, which are commonly used in automotive drive shafts, maintain a constant velocity of rotation while accommodating changing operating angles. These flexible couplings enable smooth power transmission and reduce vibrations and wear caused by speed and torque variations.
2. Slip Joints:
In some drive shaft designs, slip joints are incorporated to handle variations in length and accommodate changes in distance between the driving and driven components. A slip joint consists of an inner and outer tubular section with splines or a telescoping mechanism. As the drive shaft experiences changes in length due to suspension movement or other factors, the slip joint allows the shaft to extend or compress without affecting the power transmission. By allowing axial movement, slip joints help prevent binding or excessive stress on the drive shaft during variations in speed and torque, ensuring smooth operation.
3. Balancing:
Drive shafts undergo balancing procedures to optimize their performance and minimize vibrations caused by speed and torque variations. Imbalances in the drive shaft can lead to vibrations, which not only affect the comfort of vehicle occupants but also increase wear and tear on the shaft and its associated components. Balancing involves redistributing mass along the drive shaft to achieve even weight distribution, reducing vibrations and improving overall performance. Dynamic balancing, which typically involves adding or removing small weights, ensures that the drive shaft operates smoothly even under varying speeds and torque loads.
4. Material Selection and Design:
The selection of materials and the design of drive shafts play a crucial role in handling variations in speed and torque. Drive shafts are typically made from high-strength materials, such as steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their ability to withstand the forces and stresses associated with varying operating conditions. The diameter and wall thickness of the drive shaft are also carefully determined to ensure sufficient strength and stiffness. Additionally, the design incorporates considerations for factors such as critical speed, torsional rigidity, and resonance avoidance, which help maintain stability and performance during speed and torque variations.
5. Lubrication:
Proper lubrication is essential for drive shafts to handle variations in speed and torque. Lubricating the joints, such as U-joints or CV joints, reduces friction and heat generated during operation, ensuring smooth movement and minimizing wear. Adequate lubrication also helps prevent the binding of components, allowing the drive shaft to accommodate speed and torque variations more effectively. Regular lubrication maintenance is necessary to ensure optimal performance and extend the lifespan of the drive shaft.
6. System Monitoring:
Monitoring the performance of the drive shaft system is important to identify any issues related to variations in speed and torque. Unusual vibrations, noises, or changes in power transmission can indicate potential problems with the drive shaft. Regular inspections and maintenance checks allow for the early detection and resolution of issues, helping to prevent further damage and ensure the drive shaft continues to handle speed and torque variations effectively.
In summary, drive shafts handle variations in speed and torque during operation through the use of flexible couplings, slip joints, balancing procedures, appropriate material selection and design, lubrication, and system monitoring. These mechanisms and practices allow the drive shaft to accommodate misalignment, changes in length, and variations in power demands, ensuring efficient power transmission, smooth operation, and reduced wear and tear in various applications.

How do drive shafts handle variations in load and vibration during operation?
Drive shafts are designed to handle variations in load and vibration during operation by employing various mechanisms and features. These mechanisms help ensure smooth power transmission, minimize vibrations, and maintain the structural integrity of the drive shaft. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts handle load and vibration variations:
1. Material Selection and Design:
Drive shafts are typically made from materials with high strength and stiffness, such as steel alloys or composite materials. The material selection and design take into account the anticipated loads and operating conditions of the application. By using appropriate materials and optimizing the design, drive shafts can withstand the expected variations in load without experiencing excessive deflection or deformation.
2. Torque Capacity:
Drive shafts are designed with a specific torque capacity that corresponds to the expected loads. The torque capacity takes into account factors such as the power output of the driving source and the torque requirements of the driven components. By selecting a drive shaft with sufficient torque capacity, variations in load can be accommodated without exceeding the drive shaft’s limits and risking failure or damage.
3. Dynamic Balancing:
During the manufacturing process, drive shafts can undergo dynamic balancing. Imbalances in the drive shaft can result in vibrations during operation. Through the balancing process, weights are strategically added or removed to ensure that the drive shaft spins evenly and minimizes vibrations. Dynamic balancing helps to mitigate the effects of load variations and reduces the potential for excessive vibrations in the drive shaft.
4. Dampers and Vibration Control:
Drive shafts can incorporate dampers or vibration control mechanisms to further minimize vibrations. These devices are typically designed to absorb or dissipate vibrations that may arise from load variations or other factors. Dampers can be in the form of torsional dampers, rubber isolators, or other vibration-absorbing elements strategically placed along the drive shaft. By managing and attenuating vibrations, drive shafts ensure smooth operation and enhance overall system performance.
5. CV Joints:
Constant Velocity (CV) joints are often used in drive shafts to accommodate variations in operating angles and to maintain a constant speed. CV joints allow the drive shaft to transmit power even when the driving and driven components are at different angles. By accommodating variations in operating angles, CV joints help minimize the impact of load variations and reduce potential vibrations that may arise from changes in the driveline geometry.
6. Lubrication and Maintenance:
Proper lubrication and regular maintenance are essential for drive shafts to handle load and vibration variations effectively. Lubrication helps reduce friction between moving parts, minimizing wear and heat generation. Regular maintenance, including inspection and lubrication of joints, ensures that the drive shaft remains in optimal condition, reducing the risk of failure or performance degradation due to load variations.
7. Structural Rigidity:
Drive shafts are designed to have sufficient structural rigidity to resist bending and torsional forces. This rigidity helps maintain the integrity of the drive shaft when subjected to load variations. By minimizing deflection and maintaining structural integrity, the drive shaft can effectively transmit power and handle variations in load without compromising performance or introducing excessive vibrations.
8. Control Systems and Feedback:
In some applications, drive shafts may be equipped with control systems that actively monitor and adjust parameters such as torque, speed, and vibration. These control systems use sensors and feedback mechanisms to detect variations in load or vibrations and make real-time adjustments to optimize performance. By actively managing load variations and vibrations, drive shafts can adapt to changing operating conditions and maintain smooth operation.
In summary, drive shafts handle variations in load and vibration during operation through careful material selection and design, torque capacity considerations, dynamic balancing, integration of dampers and vibration control mechanisms, utilization of CV joints, proper lubrication and maintenance, structural rigidity, and, in some cases, control systems and feedback mechanisms. By incorporating these features and mechanisms, drive shafts ensure reliable and efficient power transmission while minimizing the impact of load variations and vibrations on overall system performance.

What benefits do drive shafts offer for different types of vehicles and equipment?
Drive shafts offer several benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment. They play a crucial role in power transmission and contribute to the overall performance, efficiency, and functionality of various systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of the benefits that drive shafts provide:
1. Efficient Power Transmission:
Drive shafts enable efficient power transmission from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. By connecting the engine or motor to the driven system, drive shafts efficiently transfer rotational power, allowing vehicles and equipment to perform their intended functions. This efficient power transmission ensures that the power generated by the engine is effectively utilized, optimizing the overall performance and productivity of the system.
2. Versatility:
Drive shafts offer versatility in their applications. They are used in various types of vehicles, including cars, trucks, motorcycles, and off-road vehicles. Additionally, drive shafts are employed in a wide range of equipment and machinery, such as agricultural machinery, construction equipment, industrial machinery, and marine vessels. The ability to adapt to different types of vehicles and equipment makes drive shafts a versatile component for power transmission.
3. Torque Handling:
Drive shafts are designed to handle high levels of torque. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine or power source. Drive shafts are engineered to efficiently transmit this torque without excessive twisting or bending. By effectively handling torque, drive shafts ensure that the power generated by the engine is reliably transferred to the wheels or driven components, enabling vehicles and equipment to overcome resistance, such as heavy loads or challenging terrains.
4. Flexibility and Compensation:
Drive shafts provide flexibility and compensation for angular movement and misalignment. In vehicles, drive shafts accommodate the movement of the suspension system, allowing the wheels to move up and down independently. This flexibility ensures a constant power transfer even when the vehicle encounters uneven terrain. Similarly, in machinery, drive shafts compensate for misalignment between the engine or motor and the driven components, ensuring smooth power transmission and preventing excessive stress on the drivetrain.
5. Weight Reduction:
Drive shafts contribute to weight reduction in vehicles and equipment. Compared to other forms of power transmission, such as belt drives or chain drives, drive shafts are typically lighter in weight. This reduction in weight helps improve fuel efficiency in vehicles and reduces the overall weight of equipment, leading to enhanced maneuverability and increased payload capacity. Additionally, lighter drive shafts contribute to a better power-to-weight ratio, resulting in improved performance and acceleration.
6. Durability and Longevity:
Drive shafts are designed to be durable and long-lasting. They are constructed using materials such as steel or aluminum, which offer high strength and resistance to wear and fatigue. Drive shafts undergo rigorous testing and quality control measures to ensure their reliability and longevity. Proper maintenance, including lubrication and regular inspections, further enhances their durability. The robust construction and long lifespan of drive shafts contribute to the overall reliability and cost-effectiveness of vehicles and equipment.
7. Safety:
Drive shafts incorporate safety features to protect operators and bystanders. In vehicles, drive shafts are often enclosed within a protective tube or housing, preventing contact with moving parts and reducing the risk of injury in the event of a failure. Similarly, in machinery, safety shields or guards are commonly installed around exposed drive shafts to minimize the potential hazards associated with rotating components. These safety measures ensure the well-being of individuals operating or working in proximity to vehicles and equipment.
In summary, drive shafts offer several benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment. They enable efficient power transmission, provide versatility in various applications, handle torque effectively, offer flexibility and compensation, contribute to weight reduction, ensure durability and longevity, and incorporate safety features. By providing these advantages, drive shafts enhance the performance, efficiency, reliability, and safety of vehicles and equipment across a wide range of industries.


editor by CX 2023-09-26
China Best Sales CZPT Factory Directly Sale Car Parts 16623, 1468577, 1697348, 2S61-3B437-AE, Front Axle Left Drive Shaft, Car Drive Shaft, CV CZPT Drive Shaft for CZPT supplier
Product Description
| PRODUCTION DETAILS |
| OEM-NUMBER: |
| FORD – OE-1142794 |
| FORD – OE-1142795 |
| FORD – OE-1333976 |
| FORD – OE-1334285 |
| FORD – OE-1341967 |
| FORD – OE-1341968 |
| FORD – OE-1359345 |
| FORD – OE-1361898 |
| FORD – OE-1416636 |
| FORD – OE-1416637 |
| FORD – OE-1416711 |
| FORD – OE-1468576 |
| FORD – OE-1468577 |
| FORD – OE-1471724 |
| FORD – OE-1478996 |
| FORD – OE-1489441 |
| FORD – OE-1489442 |
| FORD – OE-1493223 |
| FORD – OE-1506722 |
| FORD – OE-1513990 |
| FORD – OE-1513991 |
| FORD – OE-1599058 |
| FORD – OE-1599060 |
| FORD – OE-1697348 |
| FORD – OE-1697491 |
| FORD – OE-1697493 |
| FORD – OE-1833717 |
| FORD – OE-1929644 |
| FORD – OE-2S61-3B437-AB |
| FORD – OE-2S61-3B437-AC |
| FORD – OE-2S61-3B437-AD |
| FORD – OE-2S61-3B437-AE |
| FORD – OE-2S61-3B437-AF |
| FORD – OE-2S61-3B437-BB |
| FORD – OE-2S61-3B437-BC |
| FORD – OE-2S61-3B437-BD |
| FORD – OE-2S61-3B437-BE |
| FORD – OE-2S6W-3B437-AA |
| FORD – OE-2S6W-3B437-FA |
| FORD – OE-2S6W-3B437-FB |
| FORD – OE-2S6W-3B437-FC |
| TECDOC EQUIVALENTS: |
| CIFAM: 655-838 |
| DA SILVA: C6408 |
| DEPA: 3253 |
| GENERAL RICAMBI: FO3258 |
| GSP: 218141 |
| LÖBRO: 3 0571 7 |
| METELLI: 17- 0571 |
| QUINTON HAZELL: T5339 |
| RCA FRANCE: M900AN |
| SERCORE: 12617 |
| SK F: VKJC 5715 |
| SNRA: F2126 |
| SPIDAN: 24190 |
| SUITABLE CARS: |
| FORD |
| FORD Fiesta Mk5 Hatchback (JH1, JD1, JH3, JD3) (Year of Construction 11.2001 – 03.2571) |
| FORD CZPT Estate (JU2) (Year of Construction 08.2002 – 12.2012) |
| FORD Fiesta Mk5 Van (Year of Construction 10.2003 – 12.2571) |
| FORD Transit Courier Van (Year of Construction 02.2014 – …) |
| FORD Transit Courier Estate (Year of Construction 02.2014 – …) |
| FORD Tourneo Courier (Year of Construction 02.2014 – …) |
OUR ADVANTAGES:
1. GUARANTEED QUALITY
Materials with good quality are selected and tested layer by layer.
2. GOOD SERVICE
We have enthusiastic and timely online service and good after-sales service.
3. PROFESSIONAL TEAMS
We have professional teams with technology, research and production.
4. COMPETITIVE PRICE
We provide customers with better products and preferential prices.
| After-sales Service: | Professional and Responsible |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Silver, Black |
| Certification: | ISO, TS |
| Type: | Drive Shaft |
| Application Brand: | Ford |
| Samples: |
US$ 1/Set
1 Set(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
Drive shaft type
The driveshaft transfers torque from the engine to the wheels and is responsible for the smooth running of the vehicle. Its design had to compensate for differences in length and angle. It must also ensure perfect synchronization between its joints. The drive shaft should be made of high-grade materials to achieve the best balance of stiffness and elasticity. There are three main types of drive shafts. These include: end yokes, tube yokes and tapered shafts.
tube yoke
Tube yokes are shaft assemblies that use metallic materials as the main structural component. The yoke includes a uniform, substantially uniform wall thickness, a first end and an axially extending second end. The first diameter of the drive shaft is greater than the second diameter, and the yoke further includes a pair of opposing lugs extending from the second end. These lugs have holes at the ends for attaching the axle to the vehicle.
By retrofitting the driveshaft tube end into a tube fork with seat. This valve seat transmits torque to the driveshaft tube. The fillet weld 28 enhances the torque transfer capability of the tube yoke. The yoke is usually made of aluminum alloy or metal material. It is also used to connect the drive shaft to the yoke. Various designs are possible.
The QU40866 tube yoke is used with an external snap ring type universal joint. It has a cup diameter of 1-3/16″ and an overall width of 4½”. U-bolt kits are another option. It has threaded legs and locks to help secure the yoke to the drive shaft. Some performance cars and off-road vehicles use U-bolts. Yokes must be machined to accept U-bolts, and U-bolt kits are often the preferred accessory.
The end yoke is the mechanical part that connects the drive shaft to the stub shaft. These yokes are usually designed for specific drivetrain components and can be customized to your needs. Pat’s drivetrain offers OEM replacement and custom flanged yokes.
If your tractor uses PTO components, the cross and bearing kit is the perfect tool to make the connection. Additionally, cross and bearing kits help you match the correct yoke to the shaft. When choosing a yoke, be sure to measure the outside diameter of the U-joint cap and the inside diameter of the yoke ears. After taking the measurements, consult the cross and bearing identification drawings to make sure they match.
While tube yokes are usually easy to replace, the best results come from a qualified machine shop. Dedicated driveshaft specialists can assemble and balance finished driveshafts. If you are unsure of a particular aspect, please refer to the TM3000 Driveshaft and Cardan Joint Service Manual for more information. You can also consult an excerpt from the TSB3510 manual for information on angle, vibration and runout.
The sliding fork is another important part of the drive shaft. It can bend over rough terrain, allowing the U-joint to keep spinning in tougher conditions. If the slip yoke fails, you will not be able to drive and will clang. You need to replace it as soon as possible to avoid any dangerous driving conditions. So if you notice any dings, be sure to check the yoke.
If you detect any vibrations, the drivetrain may need adjustment. It’s a simple process. First, rotate the driveshaft until you find the correct alignment between the tube yoke and the sliding yoke of the rear differential. If there is no noticeable vibration, you can wait for a while to resolve the problem. Keep in mind that it may be convenient to postpone repairs temporarily, but it may cause bigger problems later.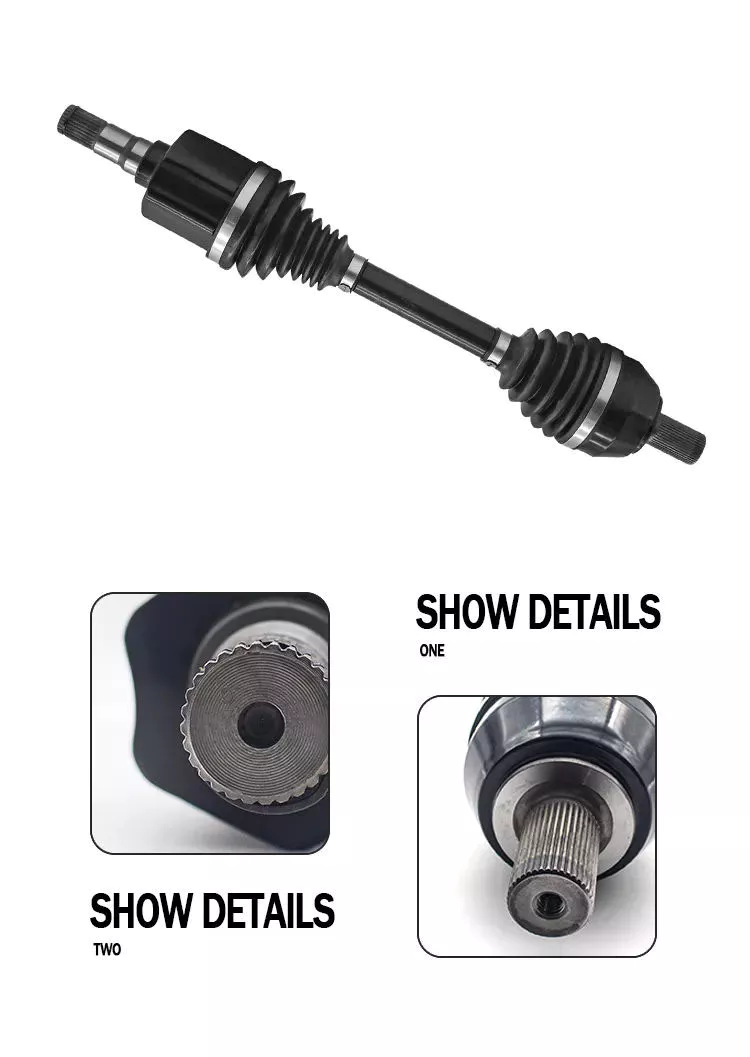
end yoke
If your driveshaft requires a new end yoke, CZPT has several drivetrain options. Our automotive end yoke inventory includes keyed and non-keyed options. If you need tapered or straight holes, we can also make them for you.
A U-bolt is an industrial fastener that has U-shaped threads on its legs. They are often used to join two heads back to back. These are convenient options to help keep drivetrain components in place when driving over rough terrain, and are generally compatible with a variety of models. U-bolts require a specially machined yoke to accept them, so be sure to order the correct size.
The sliding fork helps transfer power from the transfer case to the driveshaft. They slide in and out of the transfer case, allowing the u-joint to rotate. Sliding yokes or “slips” can be purchased separately. Whether you need a new one or just a few components to upgrade your driveshaft, 4 CZPT Parts will have the parts you need to repair your vehicle.
The end yoke is a necessary part of the drive shaft. It connects the drive train and the mating flange. They are also used in auxiliary power equipment. CZPT’s drivetrains are stocked with a variety of flanged yokes for OEM applications and custom builds. You can also find flanged yokes for constant velocity joints in our extensive inventory. If you don’t want to modify your existing drivetrain, we can even make a custom yoke for you.


editor by CX 2023-07-11
China Customed Lighting Turning Precision Stainless Steel Axle Stepped Drive Shaft with Mechanical Parts for Robot Vacuum and Motor drive shaft parts
Solution Description
Firm Profile
—–ABOUT US—–
Focuses on the research, improvement, manufacturing, sales and provider of fasteners, precision components components and a variety of metallic items.
HangZhou Bozuan Jinggong Technology Co., Ltd. was recognized on March 1, 2016. It is located in Xihu (West Lake) Dis.ang District, HangZhou Town, ZheJiang Province. It covers an area of 5600 sq. meters and focuses on the investigation, advancement, creation, income and support of fasteners, precision components components and numerous metal goods. The processed products are primarily cold heading, forging, precision turning, milling, assembly, stamping, supplemented by extrusion, upsetting and casting. In addition, we also have wealthy experience in anodizing, electroplating and heat therapy.
Product Parameters
| No. | Item | Requirements |
| one | Components | Carbon metal: 12L15, forty five#, 42CrMo Stainless metal: 303, 304, 316, 420, 630 Aluminum alloy: 6061, 6063, 5052, 7075 Copper alloy: brass H58-H63, phosphor bronze, beryllium copper Pure copper: T0 oxygen-cost-free copper, T2 red copper Plastics: nylon, bakelite, POM, PEEK |
| two | Diameter | Ø0.3-Ø50 |
| 3 | Diameter tolerance | .005mm |
| four | Hardness: | HRC/HV |
| five | Duration | .5mm-500mm |
| six | Heat treatment | Oil Quenching Large frequency quenching Carburization Vacuum Heat therapy Mesh belt CZPT warmth treatment |
| seven | Surface therapy | Electrolytic plating (barrel plating, rack plating) Electroless plating (nickel plating) Regular sandblasting and anodizing (black, silver, gray, gold, crimson) Plastic spraying, spraying metal paint, and so on. |
Operate Shop
Certifications
Research & Development
Growth intervention
Advancement capacity
Price accounting
Top quality control
Manufacturing feasibility evaluation
Task landing
Assembly service
Complicated undertaking decomposition & optimization abilities
Rapid sample
Optimization of the mildew prepare for mass goods
Product Category
Precision turning elements
Precision machining areas
Unique demands appearance components
Presentative Brand
Why Select Us?
Generate worth for clients
Assistance + Services + Manufactured in China + Technological Innovation = Resolution
★ Undertaking management, remedies
★ Rapidly designing and sampling
★ New item advancement, technological breakthrough
★ Part and machine assembly provider
Engineering capabilities
★Development intervention
★Development capacity
Value accounting
Quality handle
Manufacturing feasibility assessment
Project landing
Assembly services
★Complex undertaking decomposition & optimization capabilities
★Quick sample
★Optimization of the mildew program for mass items
|
US $0.15 / Piece | |
1,000 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Material: | Alloy Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Stepped Shaft |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| No. | Item | Specifications |
| 1 | Materials | Carbon steel: 12L15, 45#, 42CrMo; Stainless steel: 303, 304, 316, 420, 630; Aluminum alloy: 6061, 6063, 5052, 7075; Copper alloy: brass H58-H63, phosphor bronze, beryllium copper; Pure copper: T0 oxygen-free copper, T2 red copper; Plastics: nylon, bakelite, POM, PEEK; |
| 2 | Diameter | Ø0.3-Ø50 |
| 3 | Diameter tolerance | 0.005mm |
| 4 | Hardness: | HRC/HV |
| 5 | Length | 0.5mm-500mm |
| 6 | Heat treatment | Oil Quenching High frequency quenching Carburization Vacuum Heat treatment Mesh belt furnace heat treatment |
| 7 | Surface treatment | Electrolytic plating (barrel plating, rack plating); Electroless plating (nickel plating); Ordinary sandblasting and anodizing (black, silver, gray, gold, red) Plastic spraying, spraying metal paint, etc.; |
|
US $0.15 / Piece | |
1,000 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Material: | Alloy Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Stepped Shaft |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| No. | Item | Specifications |
| 1 | Materials | Carbon steel: 12L15, 45#, 42CrMo; Stainless steel: 303, 304, 316, 420, 630; Aluminum alloy: 6061, 6063, 5052, 7075; Copper alloy: brass H58-H63, phosphor bronze, beryllium copper; Pure copper: T0 oxygen-free copper, T2 red copper; Plastics: nylon, bakelite, POM, PEEK; |
| 2 | Diameter | Ø0.3-Ø50 |
| 3 | Diameter tolerance | 0.005mm |
| 4 | Hardness: | HRC/HV |
| 5 | Length | 0.5mm-500mm |
| 6 | Heat treatment | Oil Quenching High frequency quenching Carburization Vacuum Heat treatment Mesh belt furnace heat treatment |
| 7 | Surface treatment | Electrolytic plating (barrel plating, rack plating); Electroless plating (nickel plating); Ordinary sandblasting and anodizing (black, silver, gray, gold, red) Plastic spraying, spraying metal paint, etc.; |
Why Checking the Drive Shaft is Important
If you hear clicking noises while driving, your driveshaft may need repair. An experienced mechanic can tell if the noise is coming from one side or both sides. This problem is usually related to the torque converter. Read on to learn why it’s so important to have your driveshaft inspected by an auto mechanic. Here are some symptoms to look for. Clicking noises can be caused by many different things. You should first check if the noise is coming from the front or the rear of the vehicle.
hollow drive shaft
Hollow driveshafts have many benefits. They are light and reduce the overall weight of the vehicle. The largest manufacturer of these components in the world is CZPT. They also offer lightweight solutions for various applications, such as high-performance axles. CZPT driveshafts are manufactured using state-of-the-art technology. They offer excellent quality at competitive prices.
The inner diameter of the hollow shaft reduces the magnitude of the internal forces, thereby reducing the amount of torque transmitted. Unlike solid shafts, hollow shafts are getting stronger. The material inside the hollow shaft is slightly lighter, which further reduces its weight and overall torque. However, this also increases its drag at high speeds. This means that in many applications hollow driveshafts are not as efficient as solid driveshafts.
A conventional hollow drive shaft consists of a first rod 14 and a second rod 14 on both sides. The first rod is connected with the second rod, and the second rod extends in the rotation direction. The two rods are then friction welded to the central area of the hollow shaft. The frictional heat generated during the relative rotation helps to connect the two parts. Hollow drive shafts can be used in internal combustion engines and environmentally-friendly vehicles.
The main advantage of a hollow driveshaft is weight reduction. The splines of the hollow drive shaft can be designed to be smaller than the outside diameter of the hollow shaft, which can significantly reduce weight. Hollow shafts are also less likely to jam compared to solid shafts. Hollow driveshafts are expected to eventually occupy the world market for automotive driveshafts. Its advantages include fuel efficiency and greater flexibility compared to solid prop shafts.
Cardan shaft
Cardan shafts are a popular choice in industrial machinery. They are used to transmit power from one machine to another and are available in a variety of sizes and shapes. They are available in a variety of materials, including steel, copper, and aluminum. If you plan to install one of these shafts, it is important to know the different types of Cardan shafts available. To find the best option, browse the catalog.
Telescopic or “Cardan” prop shafts, also known as U-joints, are ideal for efficient torque transfer between the drive and output system. They are efficient, lightweight, and energy-efficient. They employ advanced methods, including finite element modeling (FEM), to ensure maximum performance, weight, and efficiency. Additionally, the Cardan shaft has an adjustable length for easy repositioning.
Another popular choice for driveshafts is the Cardan shaft, also known as a driveshaft. The purpose of the driveshaft is to transfer torque from the engine to the wheels. They are typically used in high-performance car engines. Some types are made of brass, iron, or steel and have unique surface designs. Cardan shafts are available in inclined and parallel configurations.
Single Cardan shafts are a common replacement for standard Cardan shafts, but if you are looking for dual Cardan shafts for your vehicle, you will want to choose the 1310 series. This type is great for lifted jeeps and requires a CV-compatible transfer case. Some even require axle spacers. The dual Cardan shafts are also designed for lifts, which means it’s a good choice for raising and lowering jeeps.
universal joint
Cardan joints are a good choice for drive shafts when operating at a constant speed. Their design allows a constant angular velocity ratio between the input and output shafts. Depending on the application, the recommended speed limit may vary depending on the operating angle, transmission power, and application. These recommendations must be based on pressure. The maximum permissible speed of the drive shaft is determined by determining the angular acceleration.
Because gimbal joints don’t require grease, they can last a long time but eventually fail. If they are poorly lubricated or dry, they can cause metal-to-metal contact. The same is true for U-joints that do not have oil filling capability. While they have a long lifespan, it can be difficult to spot warning signs that could indicate impending joint failure. To avoid this, check the drive shaft regularly.
U-joints should not exceed seventy percent of their lateral critical velocity. However, if this speed is exceeded, the part will experience unacceptable vibration, reducing its useful life. To determine the best U-joint for your application, please contact your universal joint supplier. Typically, lower speeds do not require balancing. In these cases, you should consider using a larger pitch diameter to reduce axial force.
To minimize the angular velocity and torque of the output shaft, the two joints must be in phase. Therefore, the output shaft angular displacement does not completely follow the input shaft. Instead, it will lead or lag. Figure 3 illustrates the angular velocity variation and peak displacement lead of the gimbal. The ratios are shown below. The correct torque for this application is 1360 in-Ibs.
Refurbished drive shaft
Refurbished driveshafts are a good choice for a number of reasons. They are cheaper than brand new alternatives and generally just as reliable. Driveshafts are essential to the function of any car, truck, or bus. These parts are made of hollow metal tubes. While this helps reduce weight and expense, it is vulnerable to external influences. If this happens, it may crack or bend. If the shaft suffers this type of damage, it can cause serious damage to the transmission.
A car’s driveshaft is a critical component that transmits torque from the engine to the wheels. A1 Drive Shaft is a global supplier of automotive driveshafts and related components. Their factory has the capability to refurbish and repair almost any make or model of driveshafts. Refurbished driveshafts are available for every make and model of vehicle. They can be found on the market for a variety of vehicles, including passenger cars, trucks, vans, and SUVs.
Unusual noises indicate that your driveshaft needs to be replaced. Worn U-joints and bushings can cause excessive vibration. These components cause wear on other parts of the drivetrain. If you notice any of these symptoms, please take your vehicle to the AAMCO Bay Area Center for a thorough inspection. If you suspect damage to the driveshaft, don’t wait another minute – it can be very dangerous.
The cost of replacing the drive shaft
The cost of replacing a driveshaft varies, but on average, this repair costs between $200 and $1,500. While this price may vary by vehicle, the cost of parts and labor is generally equal. If you do the repair yourself, you should know how much the parts and labor will cost before you start work. Some parts can be more expensive than others, so it’s a good idea to compare the cost of several locations before deciding where to go.
If you notice any of these symptoms, you should seek a repair shop immediately. If you are still not sure if the driveshaft is damaged, do not drive the car any distance until it is repaired. Symptoms to look for include lack of power, difficulty moving the car, squeaking, clanking, or vibrating when the vehicle is moving.
Parts used in drive shafts include center support bearings, slip joints, and U-joints. The price of the driveshaft varies by vehicle and may vary by model of the same year. Also, different types of driveshafts require different repair methods and are much more expensive. Overall, though, a driveshaft replacement costs between $300 and $1,300. The process may take about an hour, depending on the vehicle model.
Several factors can lead to the need to replace the drive shaft, including bearing corrosion, damaged seals, or other components. In some cases, the U-joint indicates that the drive shaft needs to be replaced. Even if the bearings and u-joints are in good condition, they will eventually break and require the replacement of the drive shaft. However, these parts are not cheap, and if a damaged driveshaft is a symptom of a bigger problem, you should take the time to replace the shaft.


editor by czh 2022-11-30
China Customized Precision Cylindrical Grinding Shaft Parts Machining Metal Rotor Mechanical Spindle Transmission Main Axle Shaft drive shaft electric motor
Problem: New
Warranty: 1 Yr
Relevant Industries: Manufacturing Plant, Machinery Restore Stores, Design works , Vitality & Mining, grinding shaft
Bodyweight (KG): one
Showroom Location: Germany, Viet Nam
Movie outgoing-inspection: Presented
Machinery Take a look at Report: Presented
Marketing and advertising Variety: Ordinary Merchandise
Warranty of core parts: 1 12 months
Main Factors: PLC, Motor, Bearing, Gearbox, Motor, Stress vessel, Equipment
Construction: Versatile
Substance: steel, carbon steel, Stainless Metal
Coatings: Customized
Torque Potential: Any
Product Amount: Customized
Provider: OEM Customized Services
Top quality: OEM Normal
MOQ: 10pcs
Tools: CNC Machining Centres
Surface area Remedy: Customer’s Necessity
QC Control: QC Report
Size: Buyer Designed
Shipping time: 7-ten Times
Bundle: Customer’s Particular Calls for
Packaging Specifics: 1.Plastic bag or plastic wrap inside of, carton outside2.The deal of Brass Turning Device Spare Elements as customers’ need
Port: HangZhou,HangZhou,Hong Kong
Personalized Precision Cylindrical Grinding Shaft Parts Machining Steel Rotor Mechanical Spindle Transmission Main Axle Shaft
| Location Of Origin | ZheJiang ,China |
| Product Kind | Customized Precision Cylindrical Grinding Shaft Components Machining Metallic Rotor Mechanical Spindle Transmission Major Axle Shaft |
| Surface area Treatment method | heat therapy |
| Processing Technologies | CNC turning,CNC milling,external grinding |
| Drawing Structure | PDF,DWG,phase |
| Application | Automotive, Automation, Test techniques, Sensors, Health-related, Sports, Buyer, House appliance,Electronic, Pumps, Pcs, Energy andenergy, Architecture, Printing, Food, Textile machinery, Optical, Lights, Protection and security, AOI, CZPT gear, and so forth. |
| Bundle | protective packing |
| sample | 7—10 times |
| Certificate | ISO,SGS |
| MOQ | 500pcs |
| Generation Capability | 30,000 pieces per thirty day period |
| Shipping and delivery time | 25-thirty times after obtain the pre-payments |
| Payment Phrases | T/T,Paypal,Western Union,L/C or Trade Assurance 30% deposit & harmony ahead of shipping and delivery. |
| Our Services | CNC Machining,Plastic Injection,Stamping,Die Casting,Silicone And Rubber,Aluminum Extrusion,Mould Creating,and so on |
How to Replace the Drive Shaft
Several different functions in a vehicle are critical to its functioning, but the driveshaft is probably the part that needs to be understood the most. A damaged or damaged driveshaft can damage many other auto parts. This article will explain how this component works and some of the signs that it may need repair. This article is for the average person who wants to fix their car on their own but may not be familiar with mechanical repairs or even driveshaft mechanics. You can click the link below for more information.
Repair damaged driveshafts
If you own a car, you should know that the driveshaft is an integral part of the vehicle’s driveline. They ensure efficient transmission of power from the engine to the wheels and drive. However, if your driveshaft is damaged or cracked, your vehicle will not function properly. To keep your car safe and running at peak efficiency, you should have it repaired as soon as possible. Here are some simple steps to replace the drive shaft.
First, diagnose the cause of the drive shaft damage. If your car is making unusual noises, the driveshaft may be damaged. This is because worn bushings and bearings support the drive shaft. Therefore, the rotation of the drive shaft is affected. The noise will be squeaks, dings or rattles. Once the problem has been diagnosed, it is time to repair the damaged drive shaft.
Professionals can repair your driveshaft at relatively low cost. Costs vary depending on the type of drive shaft and its condition. Axle repairs can range from $300 to $1,000. Labor is usually only around $200. A simple repair can cost between $150 and $1700. You’ll save hundreds of dollars if you’re able to fix the problem yourself. You may need to spend a few more hours educating yourself about the problem before handing it over to a professional for proper diagnosis and repair.
The cost of repairing a damaged driveshaft varies by model and manufacturer. It can cost as much as $2,000 depending on parts and labor. While labor costs can vary, parts and labor are typically around $70. On average, a damaged driveshaft repair costs between $400 and $600. However, these parts can be more expensive than that. If you don’t want to spend money on unnecessarily expensive repairs, you may need to pay a little more.
Learn how drive shafts work
While a car engine may be one of the most complex components in your vehicle, the driveshaft has an equally important job. The driveshaft transmits the power of the engine to the wheels, turning the wheels and making the vehicle move. Driveshaft torque refers to the force associated with rotational motion. Drive shafts must be able to withstand extreme conditions or they may break. Driveshafts are not designed to bend, so understanding how they work is critical to the proper functioning of the vehicle.
The drive shaft includes many components. The CV connector is one of them. This is the last stop before the wheels spin. CV joints are also known as “doughnut” joints. The CV joint helps balance the load on the driveshaft, the final stop between the engine and the final drive assembly. Finally, the axle is a single rotating shaft that transmits power from the final drive assembly to the wheels.
Different types of drive shafts have different numbers of joints. They transmit torque from the engine to the wheels and must accommodate differences in length and angle. The drive shaft of a front-wheel drive vehicle usually includes a connecting shaft, an inner constant velocity joint and an outer fixed joint. They also have anti-lock system rings and torsional dampers to help them run smoothly. This guide will help you understand the basics of driveshafts and keep your car in good shape.
The CV joint is the heart of the driveshaft, it enables the wheels of the car to move at a constant speed. The connector also helps transmit power efficiently. You can learn more about CV joint driveshafts by looking at the top 3 driveshaft questions
The U-joint on the intermediate shaft may be worn or damaged. Small deviations in these joints can cause slight vibrations and wobble. Over time, these vibrations can wear out drivetrain components, including U-joints and differential seals. Additional wear on the center support bearing is also expected. If your driveshaft is leaking oil, the next step is to check your transmission.
The drive shaft is an important part of the car. They transmit power from the engine to the transmission. They also connect the axles and CV joints. When these components are in good condition, they transmit power to the wheels. If you find them loose or stuck, it can cause the vehicle to bounce. To ensure proper torque transfer, your car needs to stay on the road. While rough roads are normal, bumps and bumps are common.
Common signs of damaged driveshafts
If your vehicle vibrates heavily underneath, you may be dealing with a faulty propshaft. This issue limits your overall control of the vehicle and cannot be ignored. If you hear this noise frequently, the problem may be the cause and should be diagnosed as soon as possible. Here are some common symptoms of a damaged driveshaft. If you experience this noise while driving, you should have your vehicle inspected by a mechanic.
A clanging sound can also be one of the signs of a damaged driveshaft. A ding may be a sign of a faulty U-joint or center bearing. This can also be a symptom of worn center bearings. To keep your vehicle safe and functioning properly, it is best to have your driveshaft inspected by a certified mechanic. This can prevent serious damage to your car.
A worn drive shaft can cause difficulty turning, which can be a major safety issue. Fortunately, there are many ways to tell if your driveshaft needs service. The first thing you can do is check the u-joint itself. If it moves too much or too little in any direction, it probably means your driveshaft is faulty. Also, rust on the bearing cap seals may indicate a faulty drive shaft.
The next time your car rattles, it might be time for a mechanic to check it out. Whether your vehicle has a manual or automatic transmission, the driveshaft plays an important role in your vehicle’s performance. When one or both driveshafts fail, it can make the vehicle unsafe or impossible to drive. Therefore, you should have your car inspected by a mechanic as soon as possible to prevent further problems.
Your vehicle should also be regularly lubricated with grease and chain to prevent corrosion. This will prevent grease from escaping and causing dirt and grease to build up. Another common sign is a dirty driveshaft. Make sure your phone is free of debris and in good condition. Finally, make sure the driveshaft chain and cover are in place. In most cases, if you notice any of these common symptoms, your vehicle’s driveshaft should be replaced.
Other signs of a damaged driveshaft include uneven wheel rotation, difficulty turning the car, and increased drag when trying to turn. A worn U-joint also inhibits the ability of the steering wheel to turn, making it more difficult to turn. Another sign of a faulty driveshaft is the shuddering noise the car makes when accelerating. Vehicles with damaged driveshafts should be inspected as soon as possible to avoid costly repairs.


editor by czh
China wholesaler High Quality Auto Transmission Parts Right Front CV Axle Drive Shaft For 2019-2020 Mercedes-Benz A200 W177 B200 W247 with Best Sales
Model: 530e xDrive, 530E
12 months: 2018-2019, 2018-2019
OE NO.: A1773357100
Car Fitment: bmw
Reference NO.: DDS218328
Content: Metal
Model Amount: A1773357100
Warranty: 3 Months
Automobile Make: For 2019-2571 Mercedes-Benz A200 W177 B200 W247
Item name: Vehicles 50 % shaft
OE Code: A1773357100
Port: Xihu (West Lake) Dis.(HangZhou), HangZhou
| Product title | Auto 50 % shaft |
| Model Amount | A1773357100 |
| Warranty | 3 months |
| quality | high top quality |
| Packing | Neutral Packaging |
| MOQ | 1 established |
| Applicable models | For 2019-2571 Mercedes-Benz A200 W177 B200 W247 |
| type | Original dismantling areas |
Different parts of the drive shaft
The driveshaft is the flexible rod that transmits torque between the transmission and the differential. The term drive shaft may also refer to a cardan shaft, a transmission shaft or a propeller shaft. Parts of the drive shaft are varied and include:
The driveshaft is a flexible rod that transmits torque from the transmission to the differential
When the driveshaft in your car starts to fail, you should seek professional help as soon as possible to fix the problem. A damaged driveshaft can often be heard. This noise sounds like “tak tak” and is usually more pronounced during sharp turns. However, if you can’t hear the noise while driving, you can check the condition of the car yourself.
The drive shaft is an important part of the automobile transmission system. It transfers torque from the transmission to the differential, which then transfers it to the wheels. The system is complex, but still critical to the proper functioning of the car. It is the flexible rod that connects all other parts of the drivetrain. The driveshaft is the most important part of the drivetrain, and understanding its function will make it easier for you to properly maintain your car.
Driveshafts are used in different vehicles, including front-wheel drive, four-wheel drive, and front-engine rear-wheel drive. Drive shafts are also used in motorcycles, locomotives and ships. Common front-engine, rear-wheel drive vehicle configurations are shown below. The type of tube used depends on the size, speed and strength of the drive shaft.
The output shaft is also supported by the output link, which has two identical supports. The upper part of the drive module supports a large tapered roller bearing, while the opposite flange end is supported by a parallel roller bearing. This ensures that the torque transfer between the differentials is efficient. If you want to learn more about car differentials, read this article.
It is also known as cardan shaft, propeller shaft or drive shaft
A propshaft or propshaft is a mechanical component that transmits rotation or torque from an engine or transmission to the front or rear wheels of a vehicle. Because the axes are not directly connected to each other, it must allow relative motion. Because of its role in propelling the vehicle, it is important to understand the components of the driveshaft. Here are some common types.
Isokinetic Joint: This type of joint guarantees that the output speed is the same as the input speed. To achieve this, it must be mounted back-to-back on a plane that bisects the drive angle. Then mount the two gimbal joints back-to-back and adjust their relative positions so that the velocity changes at one joint are offset by the other joint.
Driveshaft: The driveshaft is the transverse shaft that transmits power to the front wheels. Driveshaft: The driveshaft connects the rear differential to the transmission. The shaft is part of a drive shaft assembly that includes a drive shaft, a slip joint, and a universal joint. This shaft provides rotational torque to the drive shaft.
Dual Cardan Joints: This type of driveshaft uses two cardan joints mounted back-to-back. The center yoke replaces the intermediate shaft. For the duplex universal joint to work properly, the angle between the input shaft and the output shaft must be equal. Once aligned, the two axes will operate as CV joints. An improved version of the dual gimbal is the Thompson coupling, which offers slightly more efficiency at the cost of added complexity.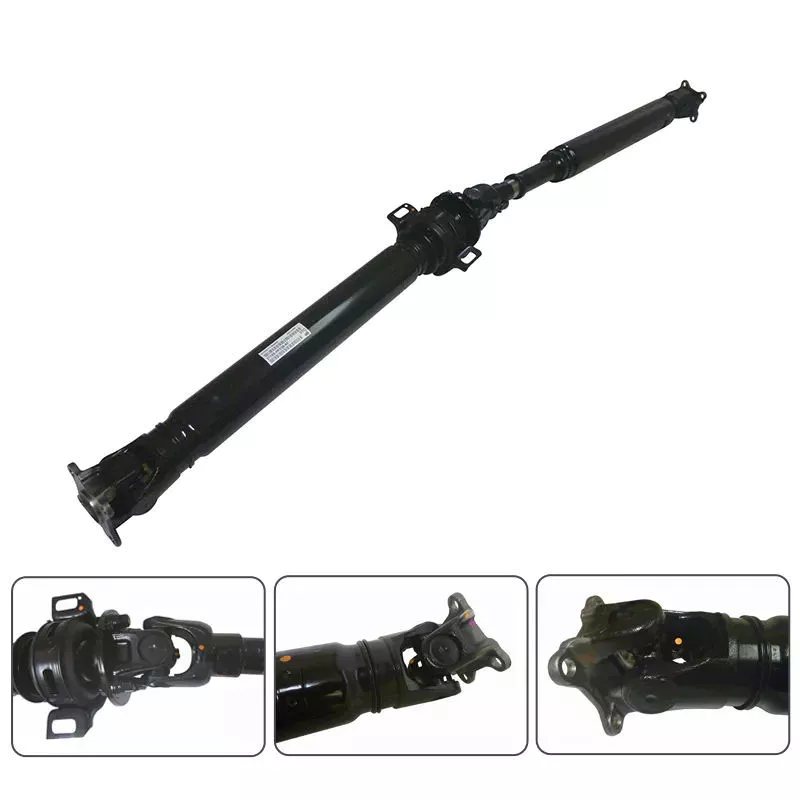
It transmits torque at different angles between driveline components
A vehicle’s driveline consists of various components that transmit power from the engine to the wheels. This includes axles, propshafts, CV joints and differentials. Together, these components transmit torque at different angles between driveline components. A car’s powertrain can only function properly if all its components work in harmony. Without these components, power from the engine would stop at the transmission, which is not the case with a car.
The CV driveshaft design provides smoother operation at higher operating angles and extends differential and transfer case life. The assembly’s central pivot point intersects the joint angle and transmits smooth rotational power and surface speed through the drivetrain. In some cases, the C.V. “U” connector. Drive shafts are not the best choice because the joint angles of the “U” joints are often substantially unequal and can cause torsional vibration.
Driveshafts also have different names, including driveshafts. A car’s driveshaft transfers torque from the transmission to the differential, which is then distributed to other driveline components. A power take-off (PTO) shaft is similar to a prop shaft. They transmit mechanical power to connected components. They are critical to the performance of any car. If any of these components are damaged, the entire drivetrain will not function properly.
A car’s powertrain can be complex and difficult to maintain. Adding vibration to the drivetrain can cause premature wear and shorten overall life. This driveshaft tip focuses on driveshaft assembly, operation, and maintenance, and how to troubleshoot any problems that may arise. Adding proper solutions to pain points can extend the life of the driveshaft. If you’re in the market for a new or used car, be sure to read this article.
it consists of several parts
“It consists of several parts” is one of seven small prints. This word consists of 10 letters and is one of the hardest words to say. However, it can be explained simply by comparing it to a cow’s kidney. The cocoa bean has several parts, and the inside of the cocoa bean before bursting has distinct lines. This article will discuss the different parts of the cocoa bean and provide a fun way to learn more about the word.
Replacement is expensive
Replacing a car’s driveshaft can be an expensive affair, and it’s not the only part that needs servicing. A damaged drive shaft can also cause other problems. This is why getting estimates from different repair shops is essential. Often, a simple repair is cheaper than replacing the entire unit. Listed below are some tips for saving money when replacing a driveshaft. Listed below are some of the costs associated with repairs:
First, learn how to determine if your vehicle needs a driveshaft replacement. Damaged driveshaft components can cause intermittent or lack of power. Additionally, improperly installed or assembled driveshaft components can cause problems with the daily operation of the car. Whenever you suspect that your car needs a driveshaft repair, seek professional advice. A professional mechanic will have the knowledge and experience needed to properly solve the problem.
Second, know which parts need servicing. Check the u-joint bushing. They should be free of crumbs and not cracked. Also, check the center support bearing. If this part is damaged, the entire drive shaft needs to be replaced. Finally, know which parts to replace. The maintenance cost of the drive shaft is significantly lower than the maintenance cost. Finally, determine if the repaired driveshaft is suitable for your vehicle.
If you suspect your driveshaft needs service, make an appointment with a repair shop as soon as possible. If you are experiencing vibration and rough riding, driveshaft repairs may be the best way to prevent costly repairs in the future. Also, if your car is experiencing unusual noise and vibration, a driveshaft repair may be a quick and easy solution. If you don’t know how to diagnose a problem with your car, you can take it to a mechanic for an appointment and a quote.


editor by czh